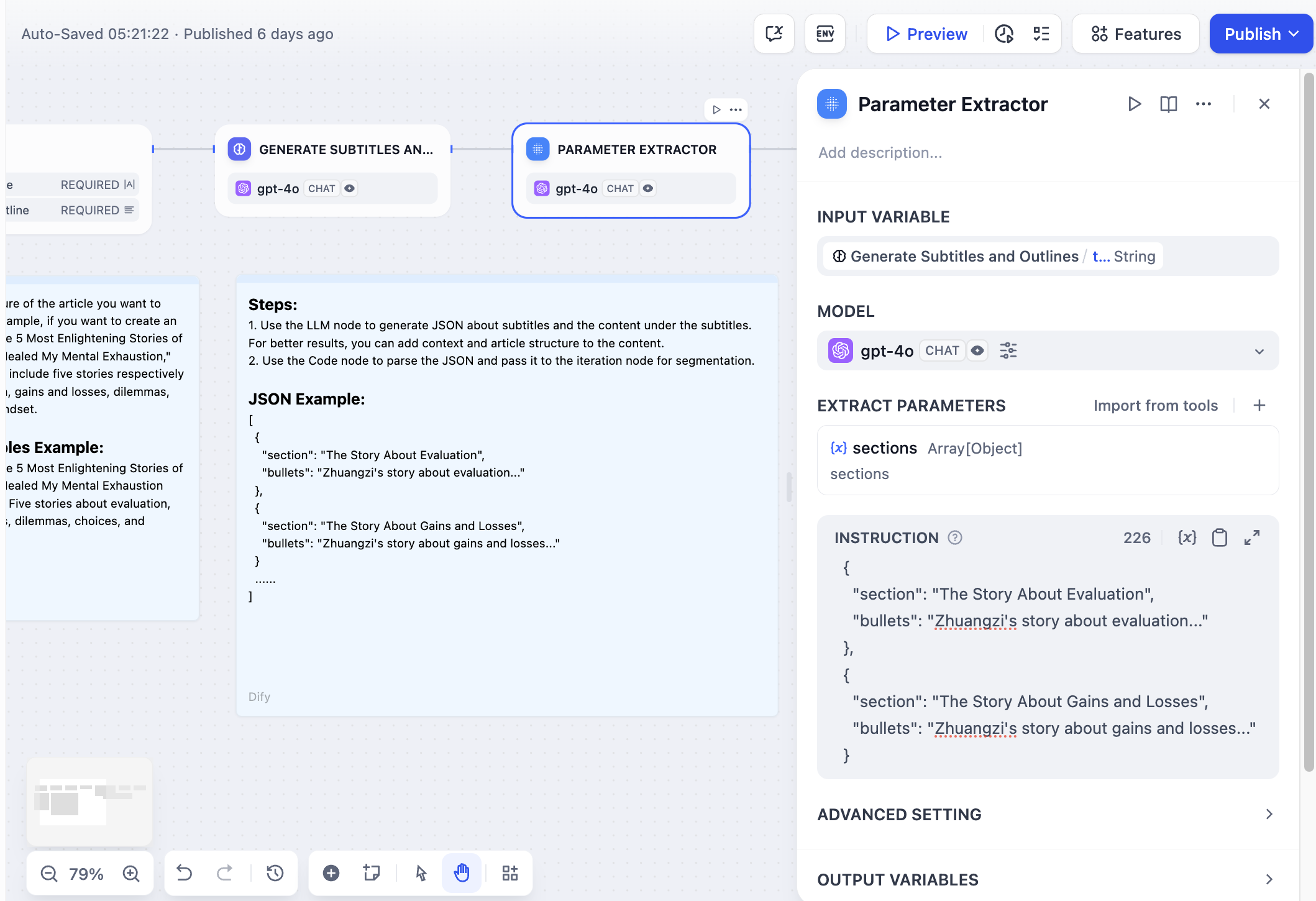
Configuration
Input and Model Selection
Select the Input Variable containing the text you want to extract parameters from. This typically comes from user input, LLM responses, or other workflow nodes. Choose a Model with strong structured output capabilities. The Parameter Extractor relies on the LLM’s ability to understand context and generate structured JSON responses.Parameter Definition
Define the parameters you want to extract by specifying:- Parameter Name - The key that will appear in the output JSON
- Data Type - String, number, boolean, array, or object
- Description - Helps the LLM understand what to extract
- Required Status - Whether the parameter must be present
Extraction Instructions
Write clear instructions describing what information to extract and how to format it. Providing examples in your instructions improves extraction accuracy and consistency for complex parameters.
Advanced Configuration
Inference Mode
Choose between two extraction approaches based on your model’s capabilities: Function Call/Tool Call uses the model’s structured output features for reliable parameter extraction with strong type compliance. Prompt-based relies on pure prompting for models that may not support function calling or when prompt-based extraction performs better.Memory
Enable memory to include conversation history when extracting parameters. This helps the LLM understand context in interactive dialogues and improves extraction accuracy for conversational workflows.Output Variables
The node provides both extracted parameters and built-in status variables: Extracted Parameters appear as individual variables matching your parameter definitions, ready for use in downstream nodes. Built-in Variables include status information:__is_success- Extraction success status (1 for success, 0 for failure)__reason- Error description when extraction fails