Configure at least one model provider in System Settings → Model Providers before using LLM nodes.
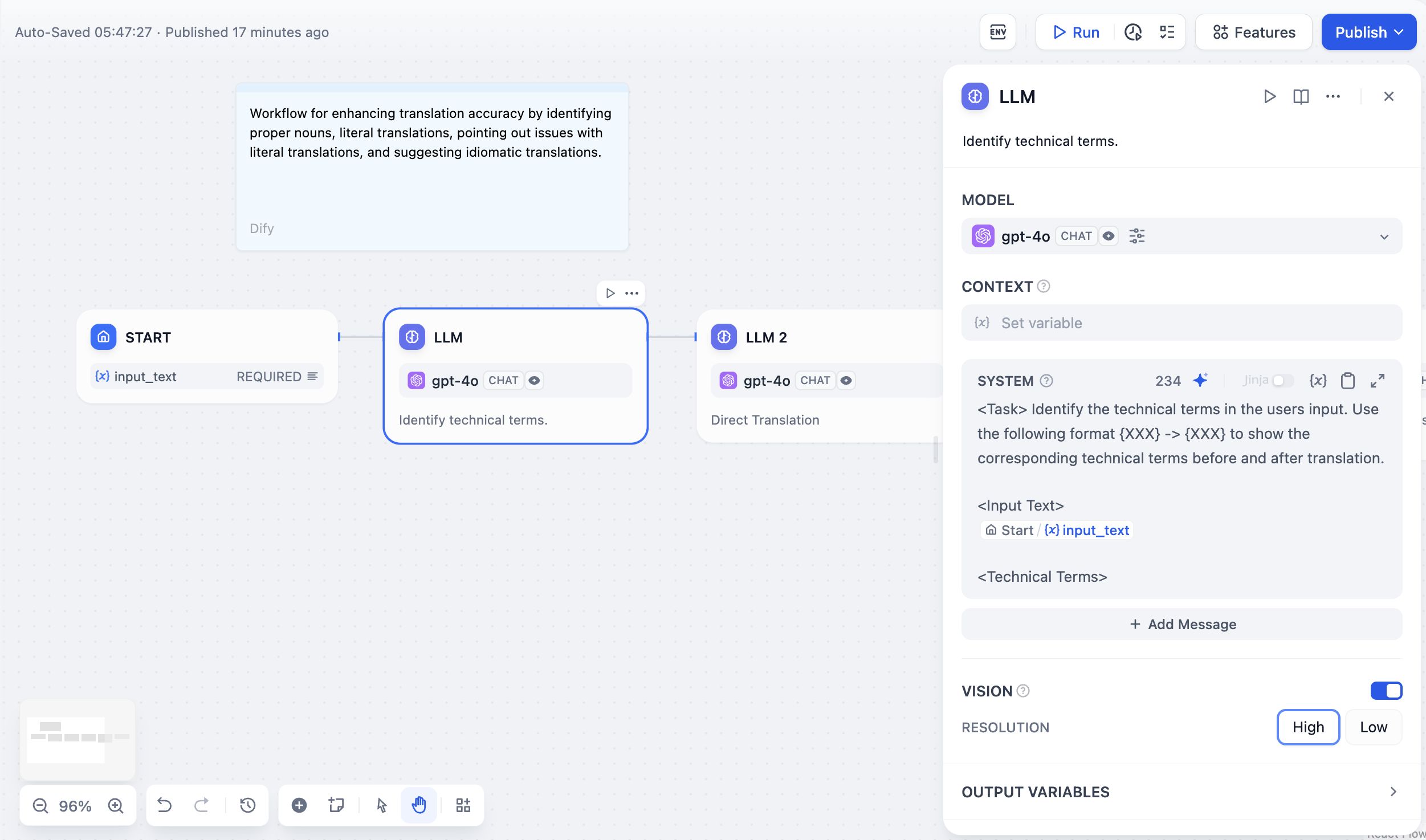
Model Selection and Parameters
Choose from any model provider you’ve configured. Different models excel at different tasks - GPT-4 and Claude 3.5 handle complex reasoning well but cost more, while GPT-3.5 Turbo balances capability with affordability. For local deployment, use Ollama, LocalAI, or Xinference.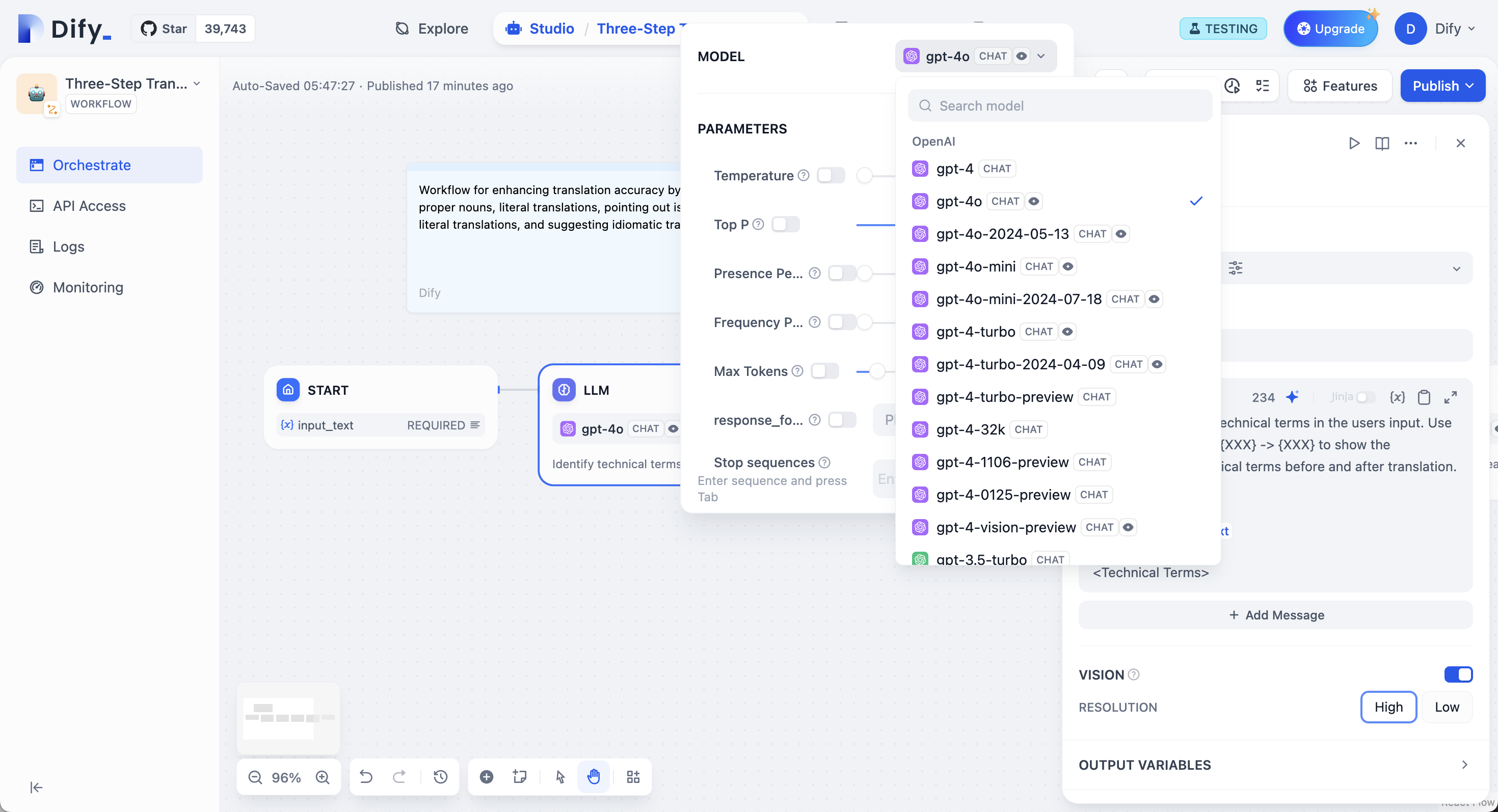
Prompt Configuration
Your interface adapts based on model type. Chat models use message roles (System for behavior, User for input, Assistant for examples), while completion models use simple text continuation. Reference workflow variables in prompts using double curly braces:{{variable_name}}. Variables are replaced with actual values before reaching the model.
Context Variables
Context variables inject external knowledge while preserving source attribution. This enables RAG applications where LLMs answer questions using your specific documents.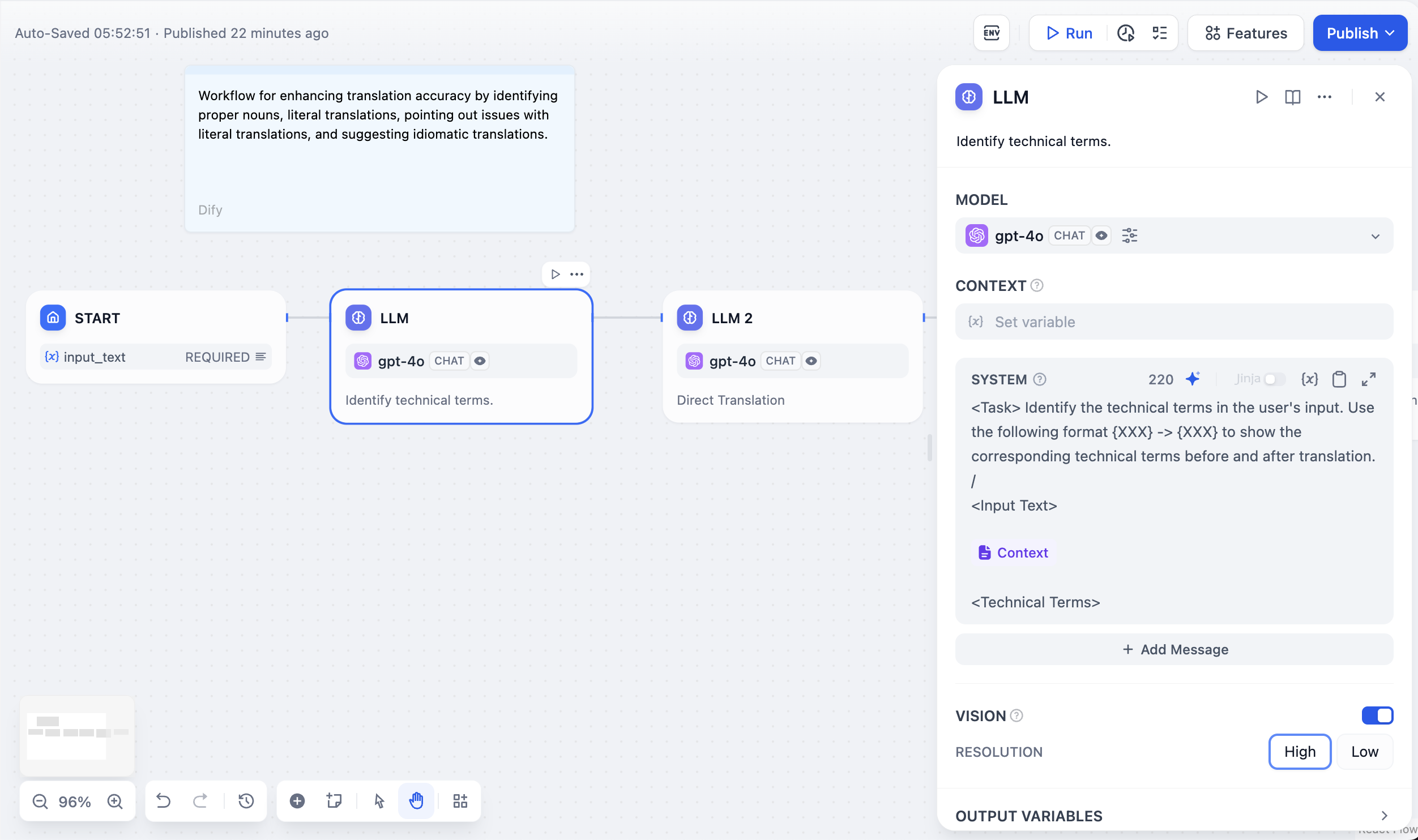
Structured Outputs
Force models to return specific data formats like JSON for programmatic use. Configure through three methods:- Visual Editor
- JSON Schema
- AI Generation
User-friendly interface for simple structures. Add fields with names and types, mark required fields, set descriptions. The editor generates JSON Schema automatically.
Memory and File Processing

USER template. Memory is node-specific and doesn’t persist between different conversations.
For File Processing, add file variables to prompts for multimodal models. GPT-4V handles images, Claude processes PDFs directly, while other models might need preprocessing.
Vision Configuration
When processing images, you can control the detail level:- High detail - Better accuracy for complex images but uses more tokens
- Low detail - Faster processing with fewer tokens for simple images
userinput.files which automatically picks up files from the User Input node.
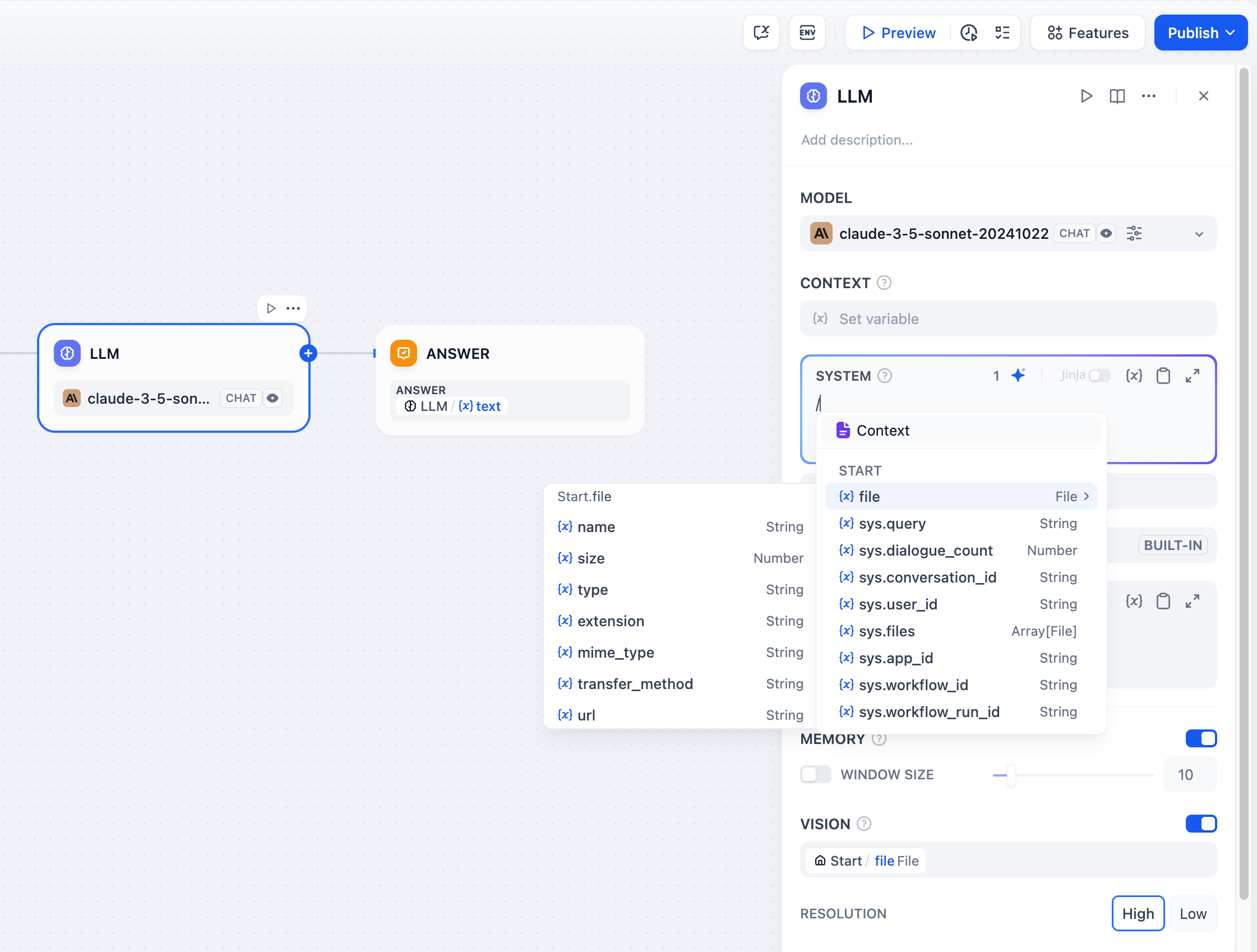
Jinja2 Template Support
LLM prompts support Jinja2 templating for advanced variable handling. When you use Jinja2 mode (edition_type: "jinja2"), you can:
Streaming Output
LLM nodes support streaming output by default. Each text chunk is yielded as aRunStreamChunkEvent, enabling real-time response display. File outputs (images, documents) are processed and saved automatically during streaming.

