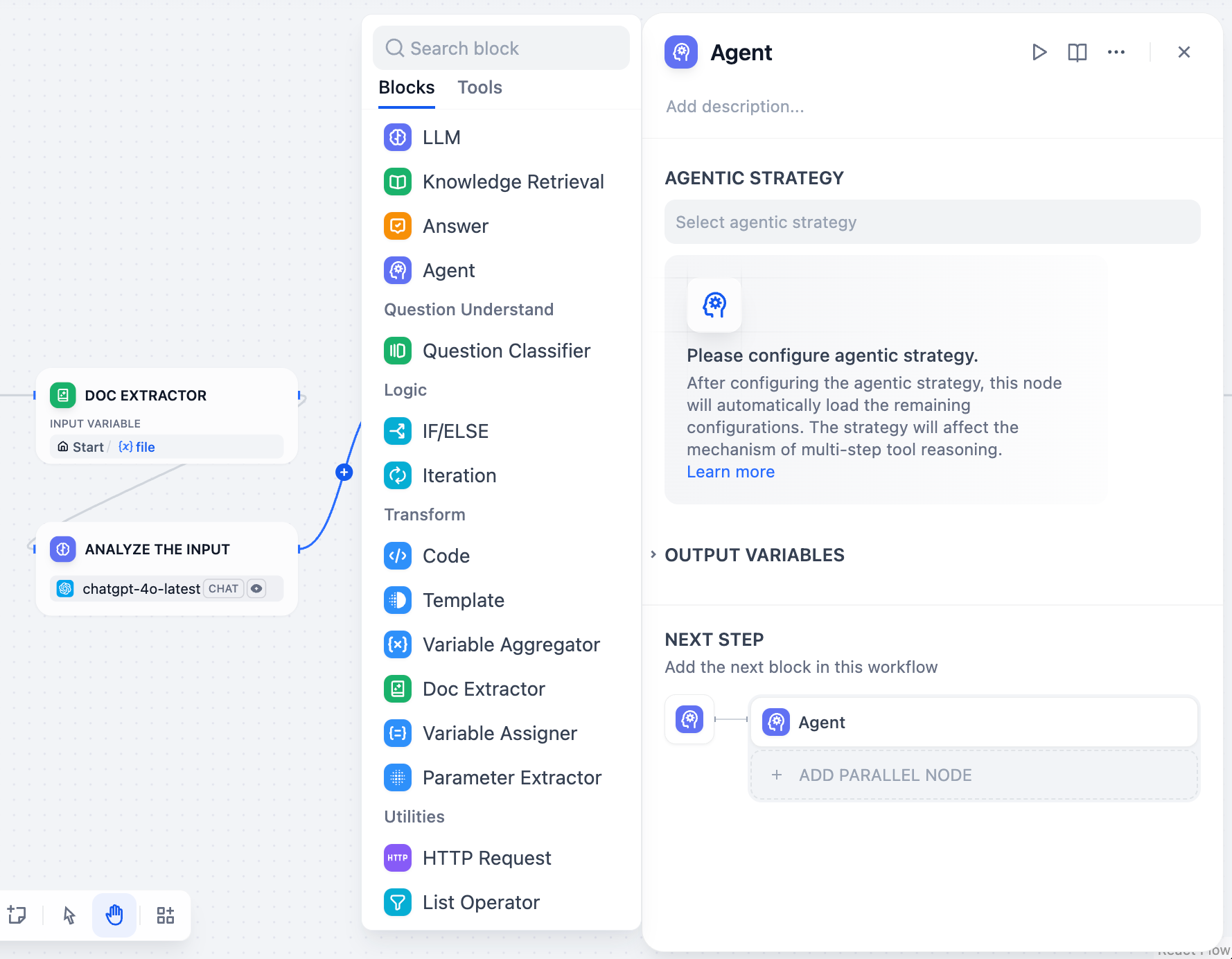
Agent Strategies
Agent strategies define how your Agent thinks and acts. Choose the approach that best matches your model’s capabilities and task requirements.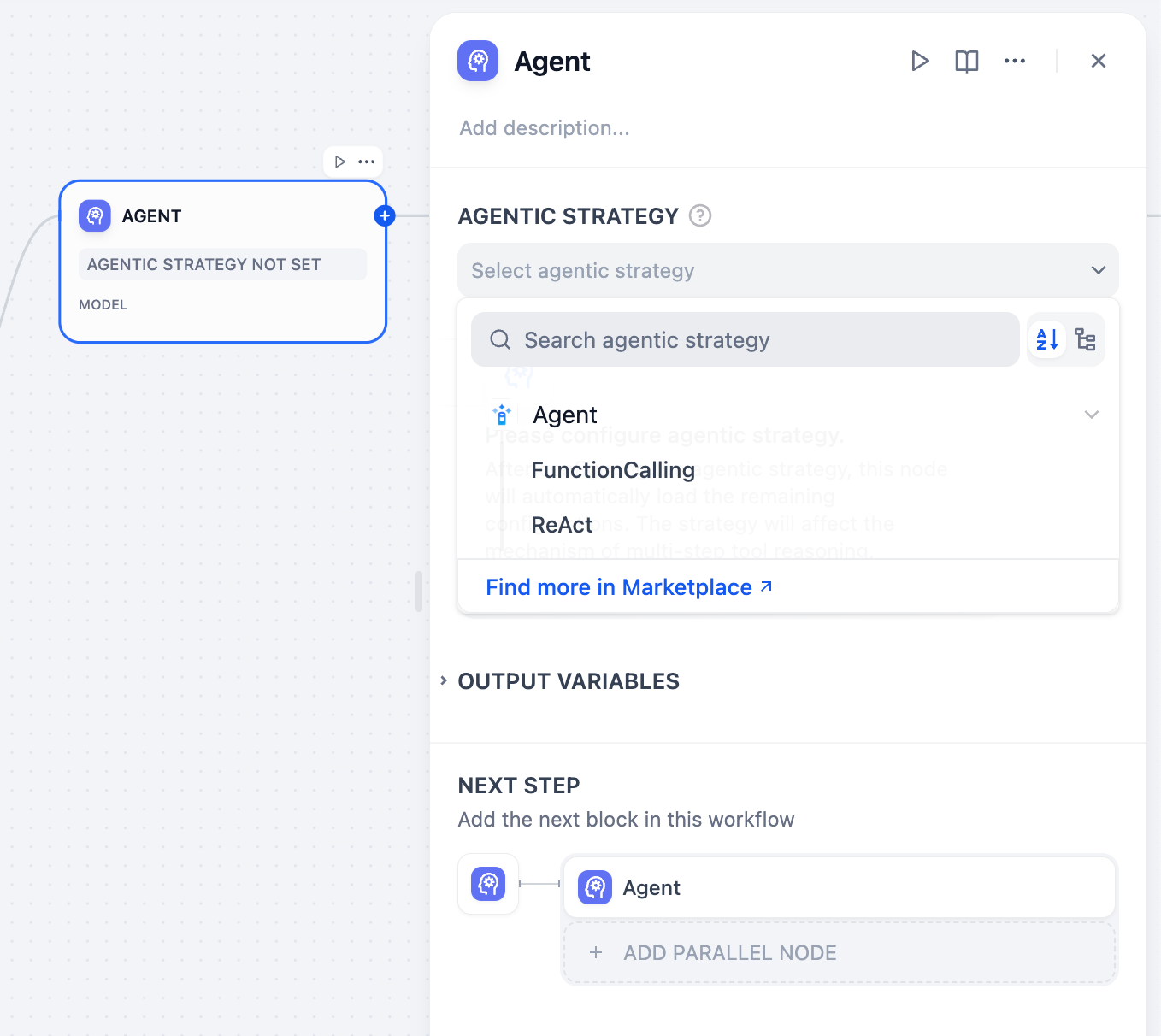
- Function Calling
- ReAct (Reason + Act)
Uses the LLM’s native function calling capabilities to directly pass tool definitions through the tools parameter. The LLM decides when and how to call tools using its built-in mechanism.Best for models like GPT-4, Claude 3.5, and other models with robust function calling support.
Install additional strategies from Marketplace → Agent Strategies or contribute custom strategies to the community repository.
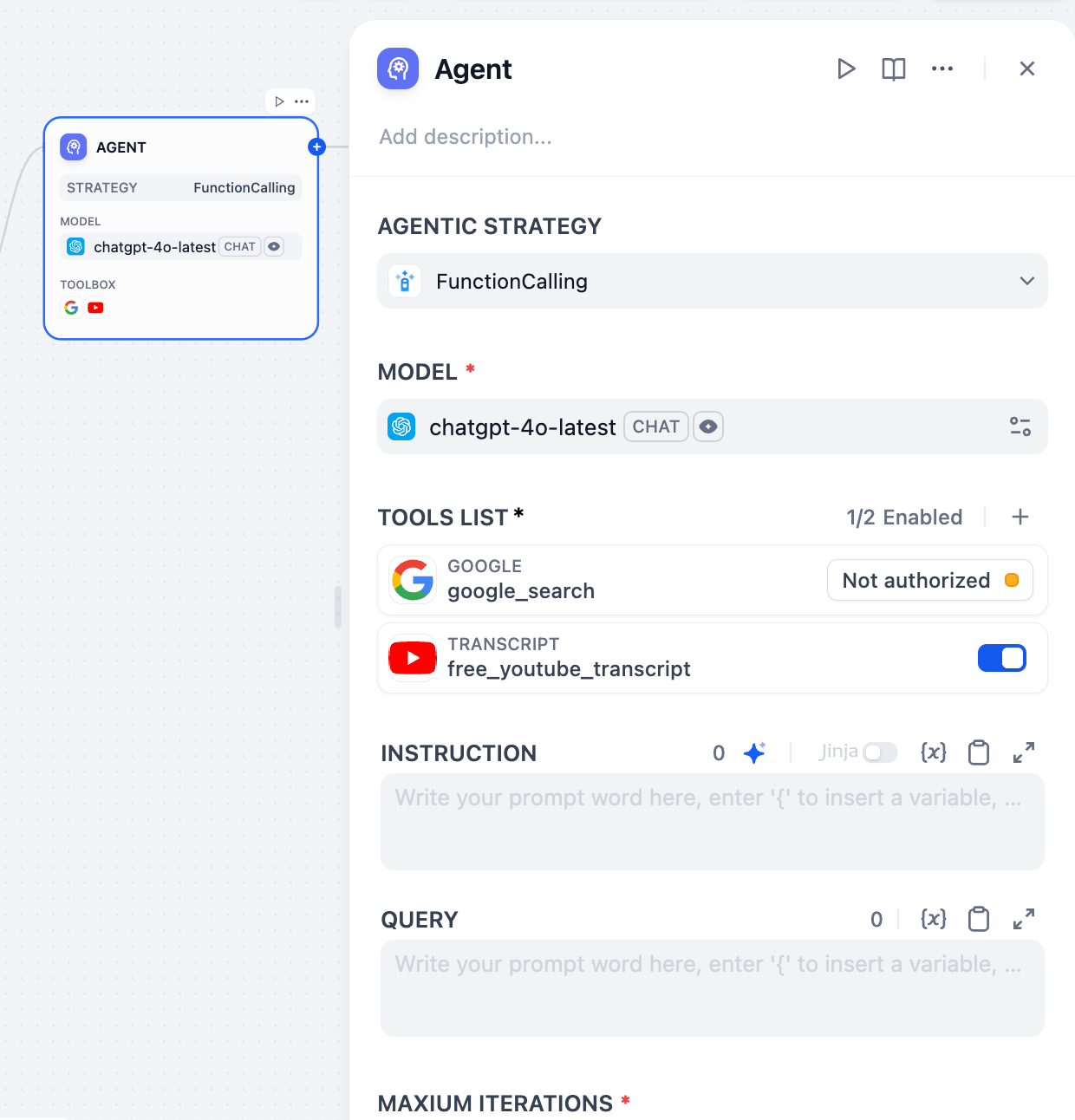
Configuration
Model Selection
Choose an LLM that supports your selected agent strategy. More capable models handle complex reasoning better but cost more per iteration. Ensure your model supports function calling if using that strategy.Tool Configuration
Configure the tools your Agent can access. Each tool requires: Authorization - API keys and credentials for external services configured in your workspace Description - Clear explanation of what the tool does and when to use it (this guides the Agent’s decision-making) Parameters - Required and optional inputs the tool accepts with proper validationInstructions and Context
Define the Agent’s role, goals, and context using natural language instructions. Use Jinja2 syntax to reference variables from upstream workflow nodes. Query specifies the user input or task the Agent should work on. This can be dynamic content from previous workflow nodes.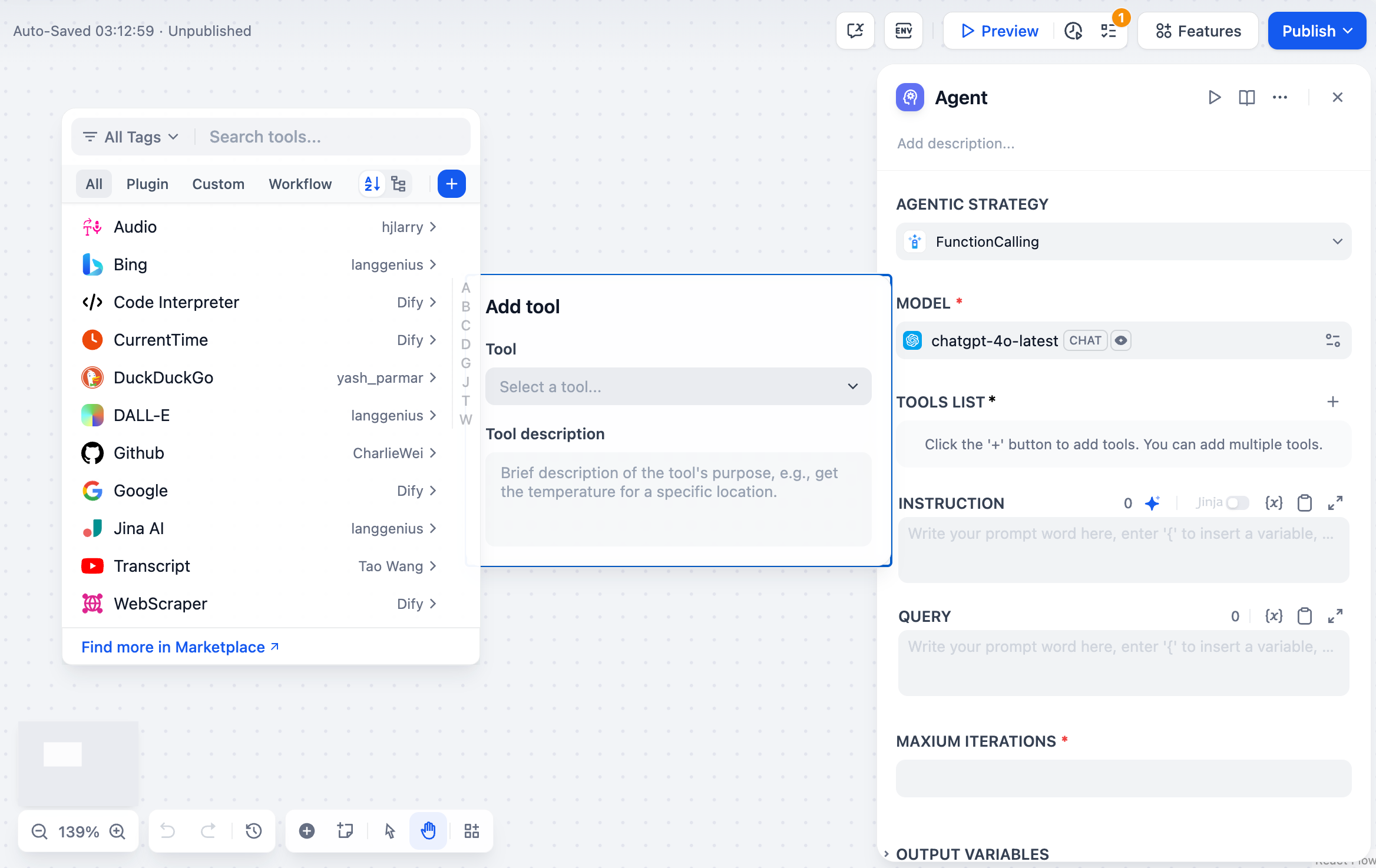
Execution Controls
Maximum Iterations sets a safety limit to prevent infinite loops. Configure based on task complexity - simple tasks need 3-5 iterations, while complex research might require 10-15. Memory controls how many previous messages the Agent remembers using TokenBufferMemory. Larger memory windows provide more context but increase token costs. This enables conversational continuity where users can reference previous actions.Tool Parameter Auto-Generation
Tools can have parameters configured as auto-generated or manual input. Auto-generated parameters (auto: false) are automatically populated by the Agent, while manual input parameters require explicit values that become part of the tool’s permanent configuration.

