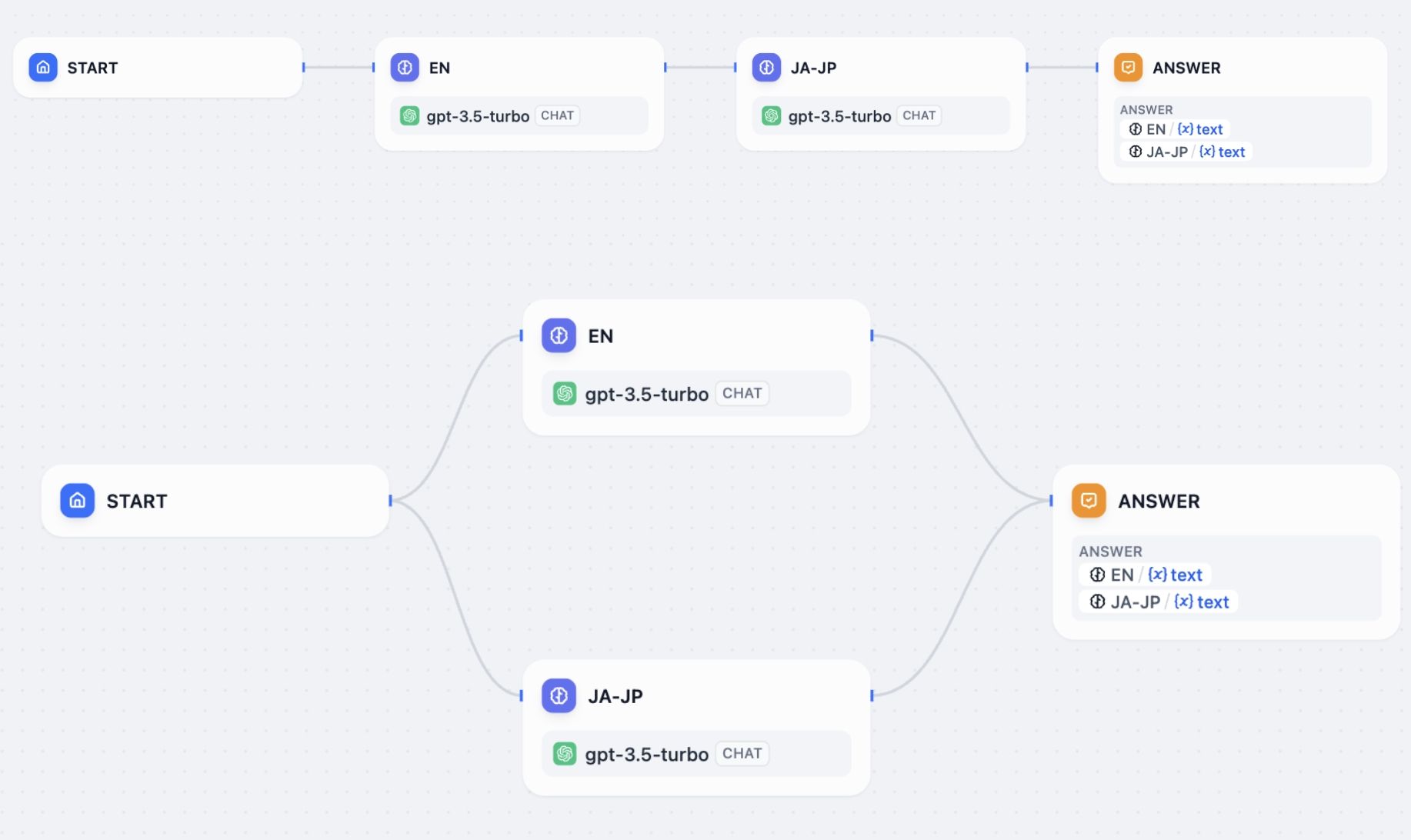
Serial vs. Parallel execution
 Flows execute differently depending on how you connect the nodes.
When you connect nodes one after another, they execute in sequence. Each node waits for the previous one to finish before starting. Each node may use variables from any node that ran before it in the chain.
Flows execute differently depending on how you connect the nodes.
When you connect nodes one after another, they execute in sequence. Each node waits for the previous one to finish before starting. Each node may use variables from any node that ran before it in the chain.
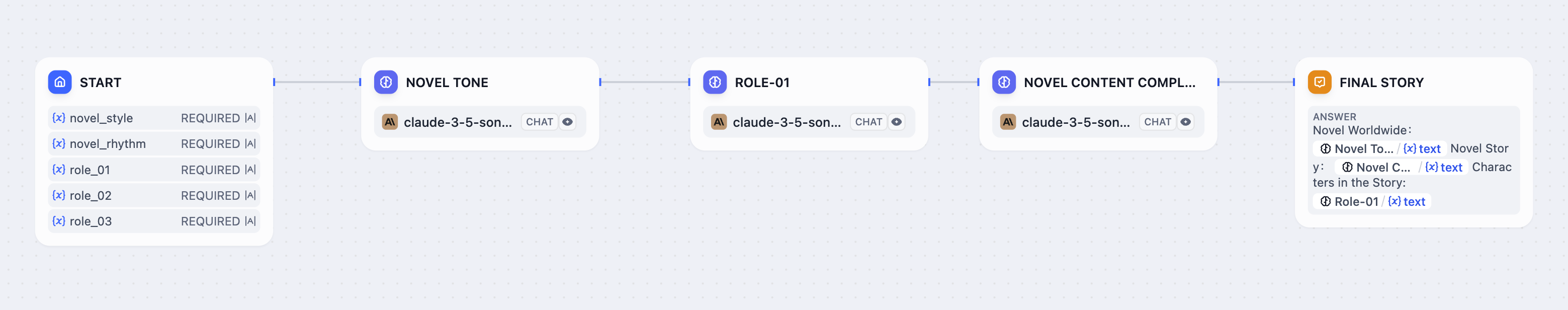 When you connect multiple nodes to the same starting node, they all run at the same time. Nodes may not reference parallel node outputs.
When you connect multiple nodes to the same starting node, they all run at the same time. Nodes may not reference parallel node outputs.
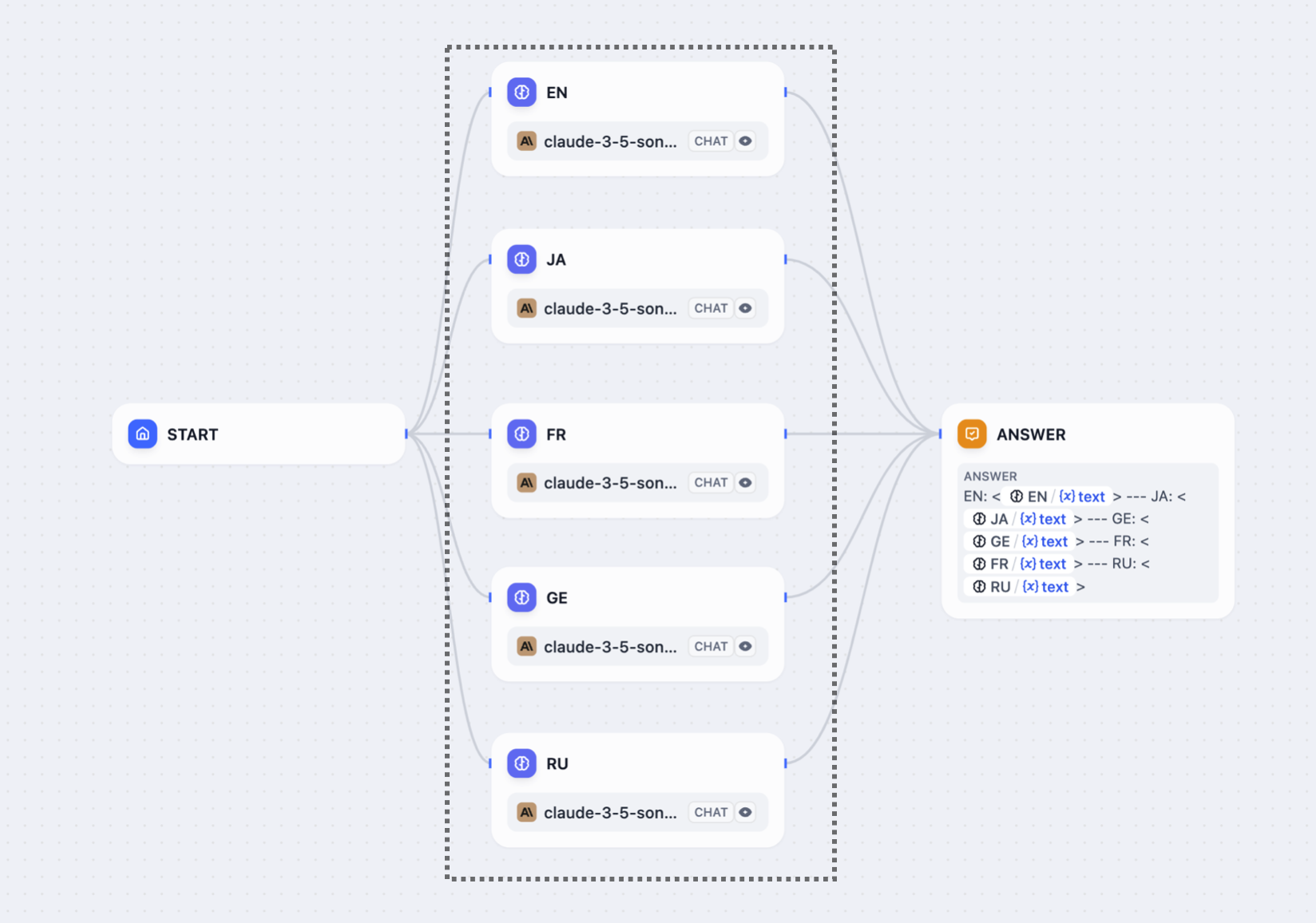
You can have a maximum of 10 parallel branches from one node, and up to 3 levels of nested parallel structures.
Variable access
In serial flows, nodes can access variables from any previous node in the chain. In parallel flows, nodes can access variables from nodes that ran before the parallel split, but they cannot access variables from other parallel nodes since they’re running simultaneously. After parallel branches finish, downstream nodes can access variables from all the parallel outputs.Answer node streaming
Answer nodes handle parallel outputs differently. When an Answer node references variables from multiple parallel branches, it streams content progressively:- Content streams up to the first unresolved variable
- Once that variable’s node completes, streaming continues to the next unresolved variable
- The order of variables in the Answer node determines the streaming sequence, not the node execution order
Node A -> Node B -> Answer with the Answer containing {{B}} then {{A}}, the Answer will wait for Node B before streaming any content, even if Node A completes first.
