⚠️ 本文档由 AI 自动翻译。如有任何不准确之处,请参考英文原版。
前置条件
- Dify 插件脚手架工具
- Python 环境(版本 ≥ 3.12)
提示:在终端中运行
dify version 以确认脚手架工具已安装。1. 初始化插件模板
运行以下命令为你的智能体插件创建开发模板:复制
dify plugin init
复制
➜ Dify Plugins Developing dify plugin init
Edit profile of the plugin
Plugin name (press Enter to next step): # Enter the plugin name
Author (press Enter to next step): Author name # Enter the plugin author
Description (press Enter to next step): Description # Enter the plugin description
---
Select the language you want to use for plugin development, and press Enter to con
BTW, you need Python 3.12+ to develop the Plugin if you choose Python.
-> python # Select Python environment
go (not supported yet)
---
Based on the ability you want to extend, we have divided the Plugin into four type
- Tool: It's a tool provider, but not only limited to tools, you can implement an
- Model: Just a model provider, extending others is not allowed.
- Extension: Other times, you may only need a simple http service to extend the fu
- Agent Strategy: Implement your own logics here, just by focusing on Agent itself
What's more, we have provided the template for you, you can choose one of them b
tool
-> agent-strategy # Select Agent strategy template
llm
text-embedding
---
Configure the permissions of the plugin, use up and down to navigate, tab to sel
Backwards Invocation:
Tools:
Enabled: [✔] You can invoke tools inside Dify if it's enabled # Enabled by default
Models:
Enabled: [✔] You can invoke models inside Dify if it's enabled # Enabled by default
LLM: [✔] You can invoke LLM models inside Dify if it's enabled # Enabled by default
Text Embedding: [✘] You can invoke text embedding models inside Dify if it'
Rerank: [✘] You can invoke rerank models inside Dify if it's enabled
...
复制
├── GUIDE.md # User guide and documentation
├── PRIVACY.md # Privacy policy and data handling guidelines
├── README.md # Project overview and setup instructions
├── _assets/ # Static assets directory
│ └── icon.svg # Agent strategy provider icon/logo
├── main.py # Main application entry point
├── manifest.yaml # Basic plugin configuration
├── provider/ # Provider configurations directory
│ └── basic_agent.yaml # Your agent provider settings
├── requirements.txt # Python dependencies list
└── strategies/ # Strategy implementation directory
├── basic_agent.py # Basic agent strategy implementation
└── basic_agent.yaml # Basic agent strategy configuration
strategies/ 目录中。
2. 开发插件
Agent 策略插件的开发围绕两个文件展开:- 插件声明:
strategies/basic_agent.yaml - 插件实现:
strategies/basic_agent.py
2.1 定义参数
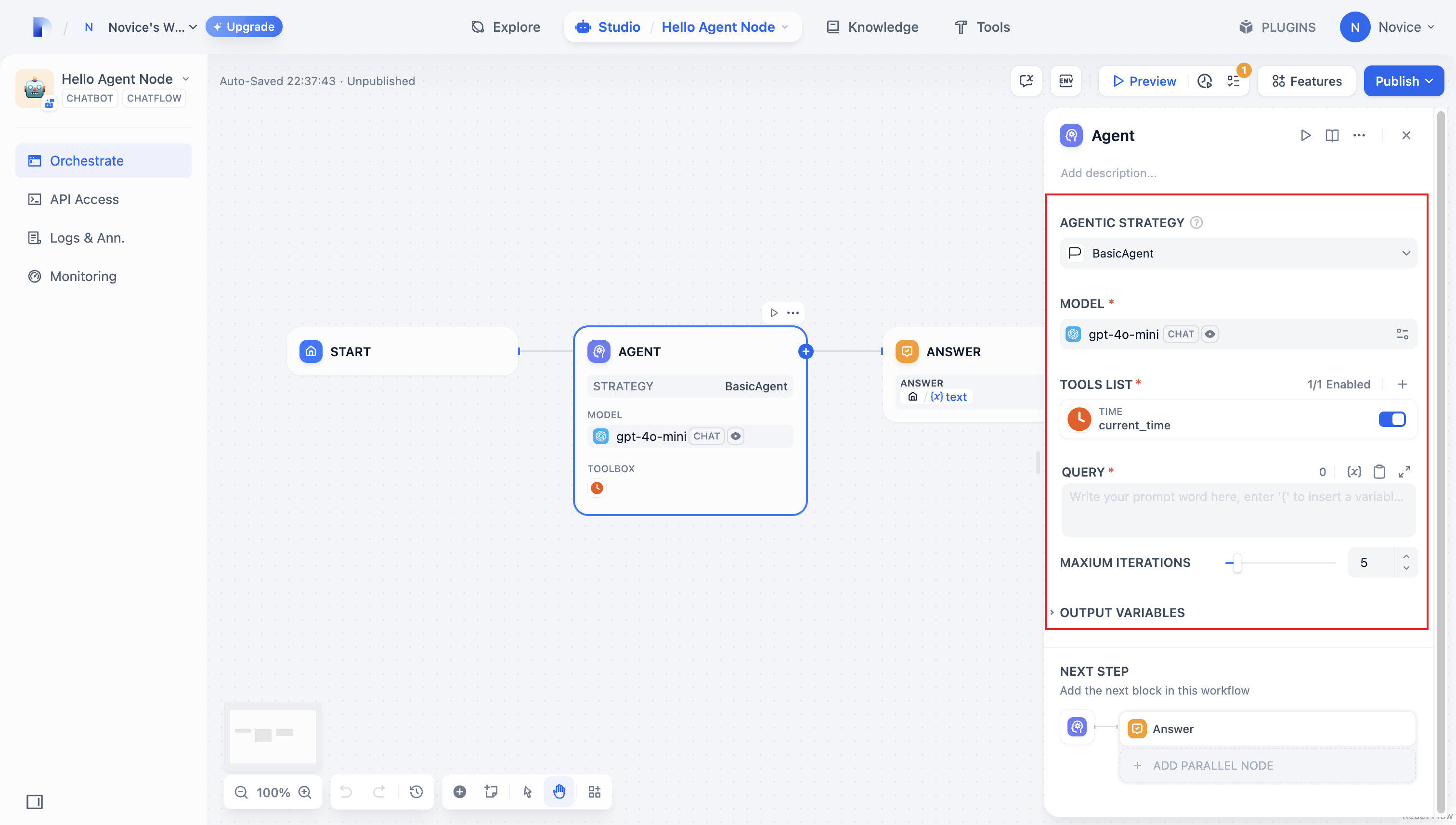
要构建智能体插件,首先在strategies/basic_agent.yaml 中指定必要的参数。这些参数定义了插件的核心功能,例如调用 LLM 或使用工具。
我们建议首先包含以下四个参数:
- model:要调用的大语言模型(例如 GPT-4、GPT-4o-mini)。
- tools:增强插件功能的工具列表。
- query:发送给模型的用户输入或提示词内容。
- maximum_iterations:防止过度计算的最大迭代次数。
复制
identity:
name: basic_agent # the name of the agent_strategy
author: novice # the author of the agent_strategy
label:
en_US: BasicAgent # the engilish label of the agent_strategy
description:
en_US: BasicAgent # the english description of the agent_strategy
parameters:
- name: model # the name of the model parameter
type: model-selector # model-type
scope: tool-call&llm # the scope of the parameter
required: true
label:
en_US: Model
zh_Hans: 模型
pt_BR: Model
- name: tools # the name of the tools parameter
type: array[tools] # the type of tool parameter
required: true
label:
en_US: Tools list
zh_Hans: 工具列表
pt_BR: Tools list
- name: query # the name of the query parameter
type: string # the type of query parameter
required: true
label:
en_US: Query
zh_Hans: 查询
pt_BR: Query
- name: maximum_iterations
type: number
required: false
default: 5
label:
en_US: Maxium Iterations
zh_Hans: 最大迭代次数
pt_BR: Maxium Iterations
max: 50 # if you set the max and min value, the display of the parameter will be a slider
min: 1
extra:
python:
source: strategies/basic_agent.py
2.2 获取参数并执行
用户填写这些基本字段后,你的插件需要处理提交的参数。在strategies/basic_agent.py 中,为智能体定义一个参数类,然后在你的逻辑中获取并应用这些参数。
验证传入参数:
复制
from dify_plugin.entities.agent import AgentInvokeMessage
from dify_plugin.interfaces.agent import AgentModelConfig, AgentStrategy, ToolEntity
from pydantic import BaseModel
class BasicParams(BaseModel):
maximum_iterations: int
model: AgentModelConfig
tools: list[ToolEntity]
query: str
复制
class BasicAgentAgentStrategy(AgentStrategy):
def _invoke(self, parameters: dict[str, Any]) -> Generator[AgentInvokeMessage]:
params = BasicParams(**parameters)
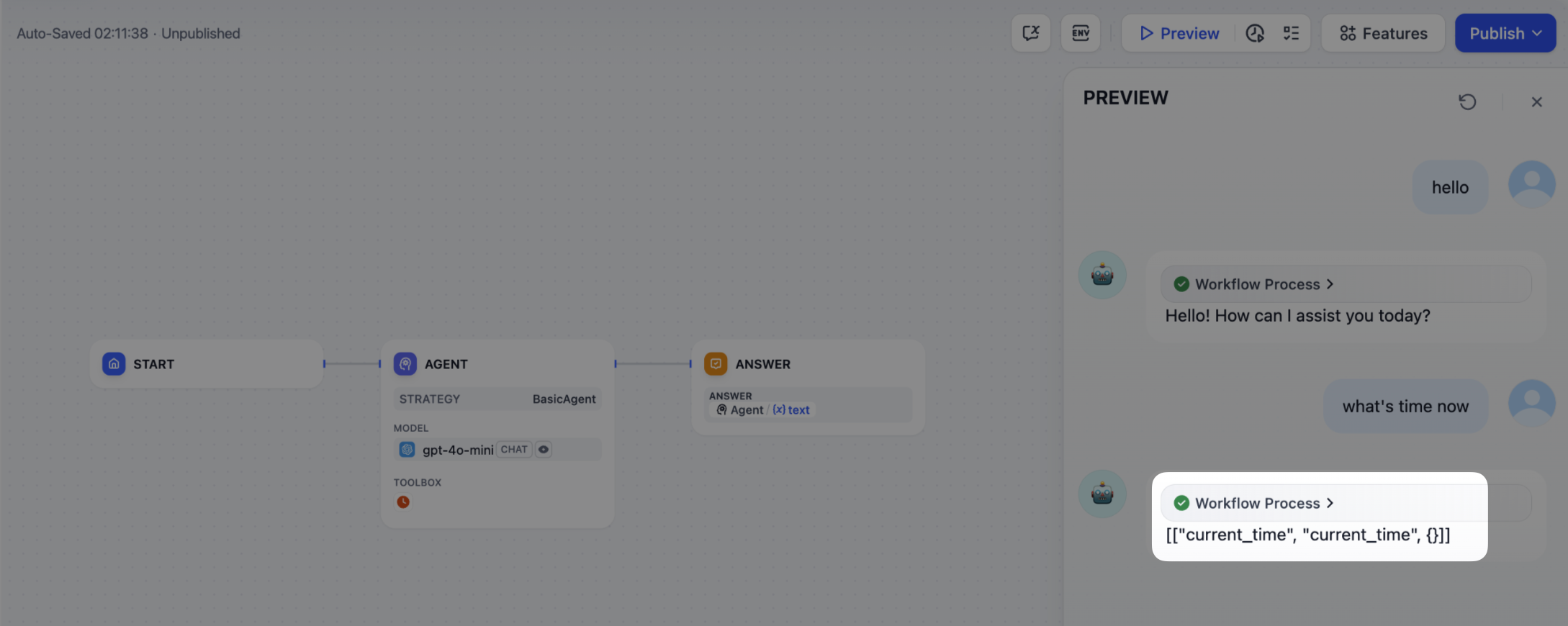
3. 调用模型
在Agent 策略插件中,调用模型是工作流的核心。你可以使用 SDK 中的session.model.llm.invoke() 高效地调用 LLM,处理文本生成、对话等任务。
如果你希望 LLM 处理工具,请确保它输出结构化参数以匹配工具的接口。换句话说,LLM 必须根据用户的指令生成工具可以接受的输入参数。
构造以下参数:
- model
- prompt_messages
- tools
- stop
- stream
复制
def invoke(
self,
model_config: LLMModelConfig,
prompt_messages: list[PromptMessage],
tools: list[PromptMessageTool] | None = None,
stop: list[str] | None = None,
stream: bool = True,
) -> Generator[LLMResultChunk, None, None] | LLMResult:...
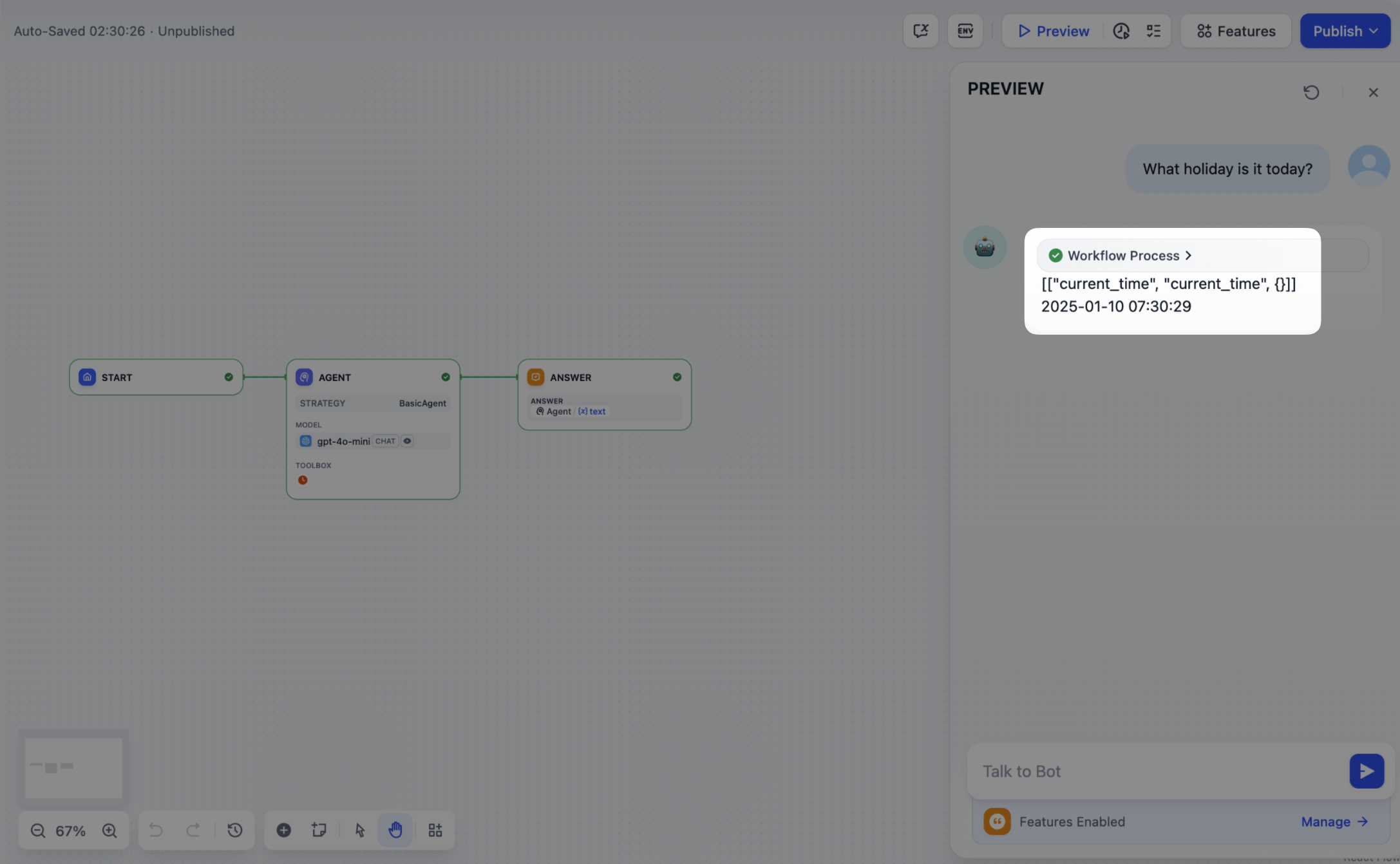
4. 处理工具
指定工具参数后,Agent 策略插件必须实际调用这些工具。使用session.tool.invoke() 来发起这些请求。
构造以下参数:
- provider
- tool_name
- parameters
复制
def invoke(
self,
provider_type: ToolProviderType,
provider: str,
tool_name: str,
parameters: dict[str, Any],
) -> Generator[ToolInvokeMessage, None, None]:...
复制
tool_instances = (
{tool.identity.name: tool for tool in params.tools} if params.tools else {}
)
for tool_call_id, tool_call_name, tool_call_args in tool_calls:
tool_instance = tool_instances[tool_call_name]
self.session.tool.invoke(
provider_type=ToolProviderType.BUILT_IN,
provider=tool_instance.identity.provider,
tool_name=tool_instance.identity.name,
parameters={**tool_instance.runtime_parameters, **tool_call_args},
)
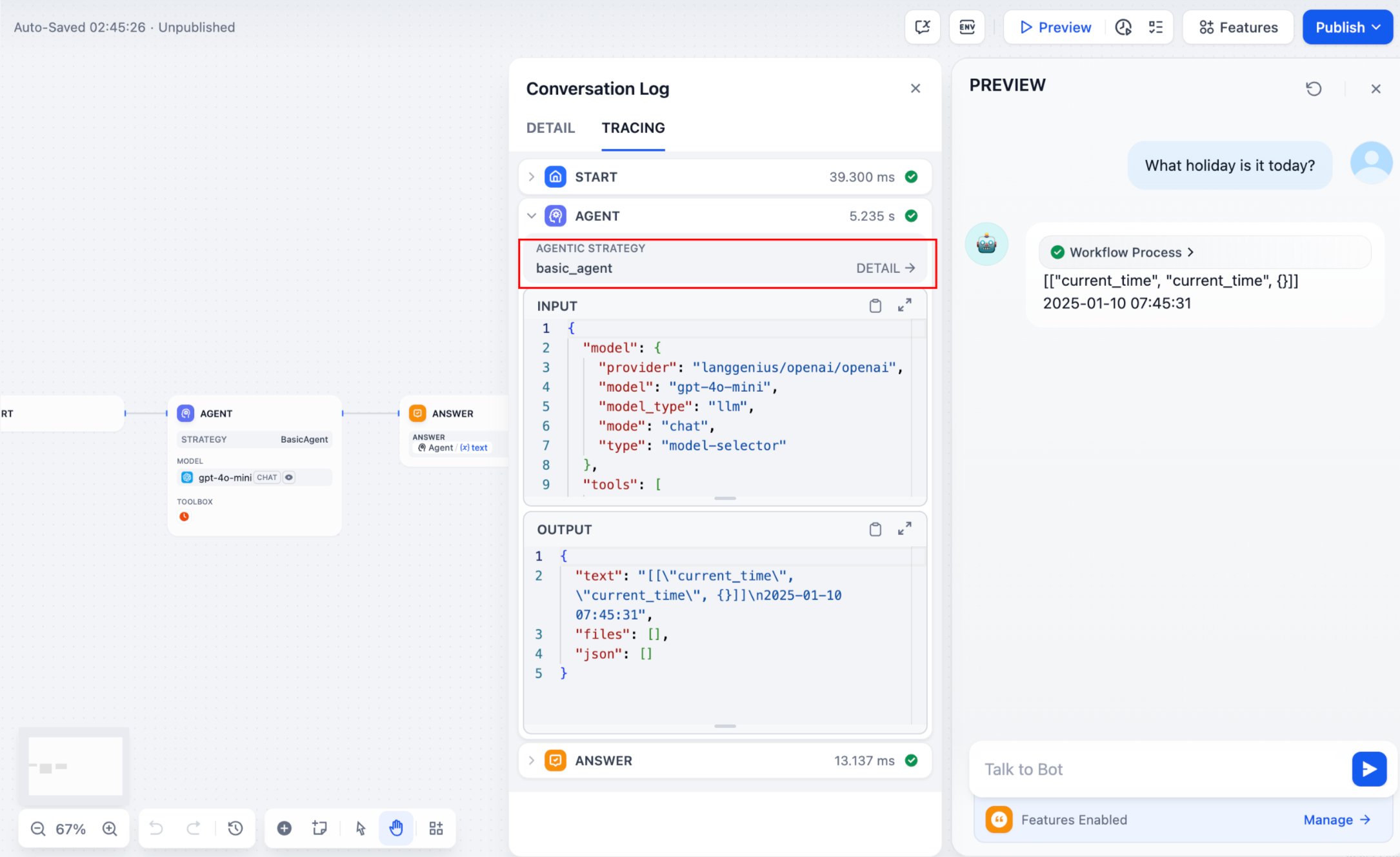
5. 创建日志
在Agent 策略插件中,通常需要多个步骤才能完成复杂任务。对于开发者来说,跟踪每个步骤的结果、分析决策过程和优化策略至关重要。使用 SDK 中的create_log_message 和 finish_log_message,你可以在调用前后记录实时状态,有助于快速诊断问题。
例如:
- 在调用模型之前记录”开始模型调用”消息,明确任务的执行进度。
- 模型响应后记录”调用成功”消息,确保模型的输出可以端到端追踪。
复制
model_log = self.create_log_message(
label=f"{params.model.model} Thought",
data={},
metadata={"start_at": model_started_at, "provider": params.model.provider},
status=ToolInvokeMessage.LogMessage.LogStatus.START,
)
yield model_log
self.session.model.llm.invoke(...)
yield self.finish_log_message(
log=model_log,
data={
"output": response,
"tool_name": tool_call_names,
"tool_input": tool_call_inputs,
},
metadata={
"started_at": model_started_at,
"finished_at": time.perf_counter(),
"elapsed_time": time.perf_counter() - model_started_at,
"provider": params.model.provider,
},
)
 如果出现多轮日志,你可以通过在日志调用中设置
如果出现多轮日志,你可以通过在日志调用中设置 parent 参数来分层组织它们,使其更易于跟踪。
参考方法:
复制
function_call_round_log = self.create_log_message(
label="Function Call Round1 ",
data={},
metadata={},
)
yield function_call_round_log
model_log = self.create_log_message(
label=f"{params.model.model} Thought",
data={},
metadata={"start_at": model_started_at, "provider": params.model.provider},
status=ToolInvokeMessage.LogMessage.LogStatus.START,
# add parent log
parent=function_call_round_log,
)
yield model_log
智能体插件功能示例代码
- 调用模型
- 处理工具
- 完整功能代码示例
调用模型
以下代码演示了如何为Agent 策略插件赋予调用模型的能力:复制
import json
from collections.abc import Generator
from typing import Any, cast
from dify_plugin.entities.agent import AgentInvokeMessage
from dify_plugin.entities.model.llm import LLMModelConfig, LLMResult, LLMResultChunk
from dify_plugin.entities.model.message import (
PromptMessageTool,
UserPromptMessage,
)
from dify_plugin.entities.tool import ToolInvokeMessage, ToolParameter, ToolProviderType
from dify_plugin.interfaces.agent import AgentModelConfig, AgentStrategy, ToolEntity
from pydantic import BaseModel
class BasicParams(BaseModel):
maximum_iterations: int
model: AgentModelConfig
tools: list[ToolEntity]
query: str
class BasicAgentAgentStrategy(AgentStrategy):
def _invoke(self, parameters: dict[str, Any]) -> Generator[AgentInvokeMessage]:
params = BasicParams(**parameters)
chunks: Generator[LLMResultChunk, None, None] | LLMResult = (
self.session.model.llm.invoke(
model_config=LLMModelConfig(**params.model.model_dump(mode="json")),
prompt_messages=[UserPromptMessage(content=params.query)],
tools=[
self._convert_tool_to_prompt_message_tool(tool)
for tool in params.tools
],
stop=params.model.completion_params.get("stop", [])
if params.model.completion_params
else [],
stream=True,
)
)
response = ""
tool_calls = []
tool_instances = (
{tool.identity.name: tool for tool in params.tools} if params.tools else {}
)
for chunk in chunks:
# check if there is any tool call
if self.check_tool_calls(chunk):
tool_calls = self.extract_tool_calls(chunk)
tool_call_names = ";".join([tool_call[1] for tool_call in tool_calls])
try:
tool_call_inputs = json.dumps(
{tool_call[1]: tool_call[2] for tool_call in tool_calls},
ensure_ascii=False,
)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
# ensure ascii to avoid encoding error
tool_call_inputs = json.dumps(
{tool_call[1]: tool_call[2] for tool_call in tool_calls}
)
print(tool_call_names, tool_call_inputs)
if chunk.delta.message and chunk.delta.message.content:
if isinstance(chunk.delta.message.content, list):
for content in chunk.delta.message.content:
response += content.data
print(content.data, end="", flush=True)
else:
response += str(chunk.delta.message.content)
print(str(chunk.delta.message.content), end="", flush=True)
if chunk.delta.usage:
# usage of the model
usage = chunk.delta.usage
yield self.create_text_message(
text=f"{response or json.dumps(tool_calls, ensure_ascii=False)}\n"
)
result = ""
for tool_call_id, tool_call_name, tool_call_args in tool_calls:
tool_instance = tool_instances[tool_call_name]
tool_invoke_responses = self.session.tool.invoke(
provider_type=ToolProviderType.BUILT_IN,
provider=tool_instance.identity.provider,
tool_name=tool_instance.identity.name,
parameters={**tool_instance.runtime_parameters, **tool_call_args},
)
if not tool_instance:
tool_invoke_responses = {
"tool_call_id": tool_call_id,
"tool_call_name": tool_call_name,
"tool_response": f"there is not a tool named {tool_call_name}",
}
else:
# invoke tool
tool_invoke_responses = self.session.tool.invoke(
provider_type=ToolProviderType.BUILT_IN,
provider=tool_instance.identity.provider,
tool_name=tool_instance.identity.name,
parameters={**tool_instance.runtime_parameters, **tool_call_args},
)
result = ""
for tool_invoke_response in tool_invoke_responses:
if tool_invoke_response.type == ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.TEXT:
result += cast(
ToolInvokeMessage.TextMessage, tool_invoke_response.message
).text
elif (
tool_invoke_response.type == ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.LINK
):
result += (
f"result link: {cast(ToolInvokeMessage.TextMessage, tool_invoke_response.message).text}."
+ " please tell user to check it."
)
elif tool_invoke_response.type in {
ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.IMAGE_LINK,
ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.IMAGE,
}:
result += (
"image has been created and sent to user already, "
+ "you do not need to create it, just tell the user to check it now."
)
elif (
tool_invoke_response.type == ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.JSON
):
text = json.dumps(
cast(
ToolInvokeMessage.JsonMessage,
tool_invoke_response.message,
).json_object,
ensure_ascii=False,
)
result += f"tool response: {text}."
else:
result += f"tool response: {tool_invoke_response.message!r}."
tool_response = {
"tool_call_id": tool_call_id,
"tool_call_name": tool_call_name,
"tool_response": result,
}
yield self.create_text_message(result)
def _convert_tool_to_prompt_message_tool(
self, tool: ToolEntity
) -> PromptMessageTool:
"""
convert tool to prompt message tool
"""
message_tool = PromptMessageTool(
name=tool.identity.name,
description=tool.description.llm if tool.description else "",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {},
"required": [],
},
)
parameters = tool.parameters
for parameter in parameters:
if parameter.form != ToolParameter.ToolParameterForm.LLM:
continue
parameter_type = parameter.type
if parameter.type in {
ToolParameter.ToolParameterType.FILE,
ToolParameter.ToolParameterType.FILES,
}:
continue
enum = []
if parameter.type == ToolParameter.ToolParameterType.SELECT:
enum = (
[option.value for option in parameter.options]
if parameter.options
else []
)
message_tool.parameters["properties"][parameter.name] = {
"type": parameter_type,
"description": parameter.llm_description or "",
}
if len(enum) > 0:
message_tool.parameters["properties"][parameter.name]["enum"] = enum
if parameter.required:
message_tool.parameters["required"].append(parameter.name)
return message_tool
def check_tool_calls(self, llm_result_chunk: LLMResultChunk) -> bool:
"""
Check if there is any tool call in llm result chunk
"""
return bool(llm_result_chunk.delta.message.tool_calls)
def extract_tool_calls(
self, llm_result_chunk: LLMResultChunk
) -> list[tuple[str, str, dict[str, Any]]]:
"""
Extract tool calls from llm result chunk
Returns:
List[Tuple[str, str, Dict[str, Any]]]: [(tool_call_id, tool_call_name, tool_call_args)]
"""
tool_calls = []
for prompt_message in llm_result_chunk.delta.message.tool_calls:
args = {}
if prompt_message.function.arguments != "":
args = json.loads(prompt_message.function.arguments)
tool_calls.append(
(
prompt_message.id,
prompt_message.function.name,
args,
)
)
return tool_calls
处理工具
以下代码展示了如何为Agent 策略插件实现模型调用并向工具发送规范化请求。复制
import json
from collections.abc import Generator
from typing import Any, cast
from dify_plugin.entities.agent import AgentInvokeMessage
from dify_plugin.entities.model.llm import LLMModelConfig, LLMResult, LLMResultChunk
from dify_plugin.entities.model.message import (
PromptMessageTool,
UserPromptMessage,
)
from dify_plugin.entities.tool import ToolInvokeMessage, ToolParameter, ToolProviderType
from dify_plugin.interfaces.agent import AgentModelConfig, AgentStrategy, ToolEntity
from pydantic import BaseModel
class BasicParams(BaseModel):
maximum_iterations: int
model: AgentModelConfig
tools: list[ToolEntity]
query: str
class BasicAgentAgentStrategy(AgentStrategy):
def _invoke(self, parameters: dict[str, Any]) -> Generator[AgentInvokeMessage]:
params = BasicParams(**parameters)
chunks: Generator[LLMResultChunk, None, None] | LLMResult = (
self.session.model.llm.invoke(
model_config=LLMModelConfig(**params.model.model_dump(mode="json")),
prompt_messages=[UserPromptMessage(content=params.query)],
tools=[
self._convert_tool_to_prompt_message_tool(tool)
for tool in params.tools
],
stop=params.model.completion_params.get("stop", [])
if params.model.completion_params
else [],
stream=True,
)
)
response = ""
tool_calls = []
tool_instances = (
{tool.identity.name: tool for tool in params.tools} if params.tools else {}
)
for chunk in chunks:
# check if there is any tool call
if self.check_tool_calls(chunk):
tool_calls = self.extract_tool_calls(chunk)
tool_call_names = ";".join([tool_call[1] for tool_call in tool_calls])
try:
tool_call_inputs = json.dumps(
{tool_call[1]: tool_call[2] for tool_call in tool_calls},
ensure_ascii=False,
)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
# ensure ascii to avoid encoding error
tool_call_inputs = json.dumps(
{tool_call[1]: tool_call[2] for tool_call in tool_calls}
)
print(tool_call_names, tool_call_inputs)
if chunk.delta.message and chunk.delta.message.content:
if isinstance(chunk.delta.message.content, list):
for content in chunk.delta.message.content:
response += content.data
print(content.data, end="", flush=True)
else:
response += str(chunk.delta.message.content)
print(str(chunk.delta.message.content), end="", flush=True)
if chunk.delta.usage:
# usage of the model
usage = chunk.delta.usage
yield self.create_text_message(
text=f"{response or json.dumps(tool_calls, ensure_ascii=False)}\n"
)
result = ""
for tool_call_id, tool_call_name, tool_call_args in tool_calls:
tool_instance = tool_instances[tool_call_name]
tool_invoke_responses = self.session.tool.invoke(
provider_type=ToolProviderType.BUILT_IN,
provider=tool_instance.identity.provider,
tool_name=tool_instance.identity.name,
parameters={**tool_instance.runtime_parameters, **tool_call_args},
)
if not tool_instance:
tool_invoke_responses = {
"tool_call_id": tool_call_id,
"tool_call_name": tool_call_name,
"tool_response": f"there is not a tool named {tool_call_name}",
}
else:
# invoke tool
tool_invoke_responses = self.session.tool.invoke(
provider_type=ToolProviderType.BUILT_IN,
provider=tool_instance.identity.provider,
tool_name=tool_instance.identity.name,
parameters={**tool_instance.runtime_parameters, **tool_call_args},
)
result = ""
for tool_invoke_response in tool_invoke_responses:
if tool_invoke_response.type == ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.TEXT:
result += cast(
ToolInvokeMessage.TextMessage, tool_invoke_response.message
).text
elif (
tool_invoke_response.type == ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.LINK
):
result += (
f"result link: {cast(ToolInvokeMessage.TextMessage, tool_invoke_response.message).text}."
+ " please tell user to check it."
)
elif tool_invoke_response.type in {
ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.IMAGE_LINK,
ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.IMAGE,
}:
result += (
"image has been created and sent to user already, "
+ "you do not need to create it, just tell the user to check it now."
)
elif (
tool_invoke_response.type == ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.JSON
):
text = json.dumps(
cast(
ToolInvokeMessage.JsonMessage,
tool_invoke_response.message,
).json_object,
ensure_ascii=False,
)
result += f"tool response: {text}."
else:
result += f"tool response: {tool_invoke_response.message!r}."
tool_response = {
"tool_call_id": tool_call_id,
"tool_call_name": tool_call_name,
"tool_response": result,
}
yield self.create_text_message(result)
def _convert_tool_to_prompt_message_tool(
self, tool: ToolEntity
) -> PromptMessageTool:
"""
convert tool to prompt message tool
"""
message_tool = PromptMessageTool(
name=tool.identity.name,
description=tool.description.llm if tool.description else "",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {},
"required": [],
},
)
parameters = tool.parameters
for parameter in parameters:
if parameter.form != ToolParameter.ToolParameterForm.LLM:
continue
parameter_type = parameter.type
if parameter.type in {
ToolParameter.ToolParameterType.FILE,
ToolParameter.ToolParameterType.FILES,
}:
continue
enum = []
if parameter.type == ToolParameter.ToolParameterType.SELECT:
enum = (
[option.value for option in parameter.options]
if parameter.options
else []
)
message_tool.parameters["properties"][parameter.name] = {
"type": parameter_type,
"description": parameter.llm_description or "",
}
if len(enum) > 0:
message_tool.parameters["properties"][parameter.name]["enum"] = enum
if parameter.required:
message_tool.parameters["required"].append(parameter.name)
return message_tool
def check_tool_calls(self, llm_result_chunk: LLMResultChunk) -> bool:
"""
Check if there is any tool call in llm result chunk
"""
return bool(llm_result_chunk.delta.message.tool_calls)
def extract_tool_calls(
self, llm_result_chunk: LLMResultChunk
) -> list[tuple[str, str, dict[str, Any]]]:
"""
Extract tool calls from llm result chunk
Returns:
List[Tuple[str, str, Dict[str, Any]]]: [(tool_call_id, tool_call_name, tool_call_args)]
"""
tool_calls = []
for prompt_message in llm_result_chunk.delta.message.tool_calls:
args = {}
if prompt_message.function.arguments != "":
args = json.loads(prompt_message.function.arguments)
tool_calls.append(
(
prompt_message.id,
prompt_message.function.name,
args,
)
)
return tool_calls
完整功能代码示例
一个完整的示例插件代码,包含调用模型、处理工具和输出多轮日志的功能:复制
import json
import time
from collections.abc import Generator
from typing import Any, cast
from dify_plugin.entities.agent import AgentInvokeMessage
from dify_plugin.entities.model.llm import LLMModelConfig, LLMResult, LLMResultChunk
from dify_plugin.entities.model.message import (
PromptMessageTool,
UserPromptMessage,
)
from dify_plugin.entities.tool import ToolInvokeMessage, ToolParameter, ToolProviderType
from dify_plugin.interfaces.agent import AgentModelConfig, AgentStrategy, ToolEntity
from pydantic import BaseModel
class BasicParams(BaseModel):
maximum_iterations: int
model: AgentModelConfig
tools: list[ToolEntity]
query: str
class BasicAgentAgentStrategy(AgentStrategy):
def _invoke(self, parameters: dict[str, Any]) -> Generator[AgentInvokeMessage]:
params = BasicParams(**parameters)
function_call_round_log = self.create_log_message(
label="Function Call Round1 ",
data={},
metadata={},
)
yield function_call_round_log
model_started_at = time.perf_counter()
model_log = self.create_log_message(
label=f"{params.model.model} Thought",
data={},
metadata={"start_at": model_started_at, "provider": params.model.provider},
status=ToolInvokeMessage.LogMessage.LogStatus.START,
parent=function_call_round_log,
)
yield model_log
chunks: Generator[LLMResultChunk, None, None] | LLMResult = (
self.session.model.llm.invoke(
model_config=LLMModelConfig(**params.model.model_dump(mode="json")),
prompt_messages=[UserPromptMessage(content=params.query)],
tools=[
self._convert_tool_to_prompt_message_tool(tool)
for tool in params.tools
],
stop=params.model.completion_params.get("stop", [])
if params.model.completion_params
else [],
stream=True,
)
)
response = ""
tool_calls = []
tool_instances = (
{tool.identity.name: tool for tool in params.tools} if params.tools else {}
)
tool_call_names = ""
tool_call_inputs = ""
for chunk in chunks:
# check if there is any tool call
if self.check_tool_calls(chunk):
tool_calls = self.extract_tool_calls(chunk)
tool_call_names = ";".join([tool_call[1] for tool_call in tool_calls])
try:
tool_call_inputs = json.dumps(
{tool_call[1]: tool_call[2] for tool_call in tool_calls},
ensure_ascii=False,
)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
# ensure ascii to avoid encoding error
tool_call_inputs = json.dumps(
{tool_call[1]: tool_call[2] for tool_call in tool_calls}
)
print(tool_call_names, tool_call_inputs)
if chunk.delta.message and chunk.delta.message.content:
if isinstance(chunk.delta.message.content, list):
for content in chunk.delta.message.content:
response += content.data
print(content.data, end="", flush=True)
else:
response += str(chunk.delta.message.content)
print(str(chunk.delta.message.content), end="", flush=True)
if chunk.delta.usage:
# usage of the model
usage = chunk.delta.usage
yield self.finish_log_message(
log=model_log,
data={
"output": response,
"tool_name": tool_call_names,
"tool_input": tool_call_inputs,
},
metadata={
"started_at": model_started_at,
"finished_at": time.perf_counter(),
"elapsed_time": time.perf_counter() - model_started_at,
"provider": params.model.provider,
},
)
yield self.create_text_message(
text=f"{response or json.dumps(tool_calls, ensure_ascii=False)}\n"
)
result = ""
for tool_call_id, tool_call_name, tool_call_args in tool_calls:
tool_instance = tool_instances[tool_call_name]
tool_invoke_responses = self.session.tool.invoke(
provider_type=ToolProviderType.BUILT_IN,
provider=tool_instance.identity.provider,
tool_name=tool_instance.identity.name,
parameters={**tool_instance.runtime_parameters, **tool_call_args},
)
if not tool_instance:
tool_invoke_responses = {
"tool_call_id": tool_call_id,
"tool_call_name": tool_call_name,
"tool_response": f"there is not a tool named {tool_call_name}",
}
else:
# invoke tool
tool_invoke_responses = self.session.tool.invoke(
provider_type=ToolProviderType.BUILT_IN,
provider=tool_instance.identity.provider,
tool_name=tool_instance.identity.name,
parameters={**tool_instance.runtime_parameters, **tool_call_args},
)
result = ""
for tool_invoke_response in tool_invoke_responses:
if tool_invoke_response.type == ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.TEXT:
result += cast(
ToolInvokeMessage.TextMessage, tool_invoke_response.message
).text
elif (
tool_invoke_response.type == ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.LINK
):
result += (
f"result link: {cast(ToolInvokeMessage.TextMessage, tool_invoke_response.message).text}."
+ " please tell user to check it."
)
elif tool_invoke_response.type in {
ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.IMAGE_LINK,
ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.IMAGE,
}:
result += (
"image has been created and sent to user already, "
+ "you do not need to create it, just tell the user to check it now."
)
elif (
tool_invoke_response.type == ToolInvokeMessage.MessageType.JSON
):
text = json.dumps(
cast(
ToolInvokeMessage.JsonMessage,
tool_invoke_response.message,
).json_object,
ensure_ascii=False,
)
result += f"tool response: {text}."
else:
result += f"tool response: {tool_invoke_response.message!r}."
tool_response = {
"tool_call_id": tool_call_id,
"tool_call_name": tool_call_name,
"tool_response": result,
}
yield self.create_text_message(result)
def _convert_tool_to_prompt_message_tool(
self, tool: ToolEntity
) -> PromptMessageTool:
"""
convert tool to prompt message tool
"""
message_tool = PromptMessageTool(
name=tool.identity.name,
description=tool.description.llm if tool.description else "",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {},
"required": [],
},
)
parameters = tool.parameters
for parameter in parameters:
if parameter.form != ToolParameter.ToolParameterForm.LLM:
continue
parameter_type = parameter.type
if parameter.type in {
ToolParameter.ToolParameterType.FILE,
ToolParameter.ToolParameterType.FILES,
}:
continue
enum = []
if parameter.type == ToolParameter.ToolParameterType.SELECT:
enum = (
[option.value for option in parameter.options]
if parameter.options
else []
)
message_tool.parameters["properties"][parameter.name] = {
"type": parameter_type,
"description": parameter.llm_description or "",
}
if len(enum) > 0:
message_tool.parameters["properties"][parameter.name]["enum"] = enum
if parameter.required:
message_tool.parameters["required"].append(parameter.name)
return message_tool
def check_tool_calls(self, llm_result_chunk: LLMResultChunk) -> bool:
"""
Check if there is any tool call in llm result chunk
"""
return bool(llm_result_chunk.delta.message.tool_calls)
def extract_tool_calls(
self, llm_result_chunk: LLMResultChunk
) -> list[tuple[str, str, dict[str, Any]]]:
"""
Extract tool calls from llm result chunk
Returns:
List[Tuple[str, str, Dict[str, Any]]]: [(tool_call_id, tool_call_name, tool_call_args)]
"""
tool_calls = []
for prompt_message in llm_result_chunk.delta.message.tool_calls:
args = {}
if prompt_message.function.arguments != "":
args = json.loads(prompt_message.function.arguments)
tool_calls.append(
(
prompt_message.id,
prompt_message.function.name,
args,
)
)
return tool_calls
6. 调试插件
完成插件的声明文件和实现代码后,在插件目录中运行python -m main 以重新启动它。接下来,确认插件运行正常。Dify 提供远程调试功能——前往插件管理获取你的调试密钥和远程服务器地址。
 返回你的插件项目,将
返回你的插件项目,将 .env.example 复制为 .env 并填入相关的远程服务器和调试密钥信息。
复制
INSTALL_METHOD=remote
REMOTE_INSTALL_URL=debug.dify.ai:5003
REMOTE_INSTALL_KEY=********-****-****-****-************
复制
python -m main
打包插件(可选)
一切正常后,你可以通过运行以下命令打包你的插件:复制
# Replace ./basic_agent/ with your actual plugin project path.
dify plugin package ./basic_agent/
google.difypkg(示例)的文件——这就是你的最终插件包。
恭喜! 你已经完整地开发、测试和打包了你的Agent 策略插件。
发布插件(可选)
你现在可以将其上传到 Dify 插件仓库。在此之前,请确保它符合插件发布指南。一旦获得批准,你的代码将合并到主分支,插件将自动在 Dify Marketplace 上线。进一步探索
复杂任务通常需要多轮思考和工具调用,通常重复模型调用 → 工具使用直到任务结束或达到最大迭代限制。在此过程中,有效管理提示词至关重要。查看完整的 Function Calling 实现,了解让模型调用外部工具并处理其输出的标准化方法。编辑此页面 | 报告问题

