Model 插件
接入预定义模型
本文档即将弃用
作为我们文档重组的一部分,此页面正在逐步淘汰。
点击此卡片跳转到包含最新信息的更新版本。
如果您在新的文档中发现任何差异或需要改进的地方,请使用页面底部的“报告问题”按钮。
-
按模型类型创建不同的模块结构
根据模型的类型(如
llm或text_embedding),在供应商模块下创建相应的子模块。确保每种模型类型有独立的逻辑分层,便于维护和扩展。 - 编写模型调用代码 在对应的模型类型模块下,创建一个与模型类型同名的 Python 文件(例如 llm.py)。在文件中定义实现具体模型逻辑的类,该类应符合系统的模型接口规范。
-
添加预定义模型配置
如果供应商提供了预定义模型,为每个模型创建与模型名称同名的
YAML文件(例如claude-3.5.yaml)。按照 AIModelEntity 的规范编写文件内容,描述模型的参数和功能。 - 测试插件 为新增的供应商功能编写单元测试和集成测试,确保所有功能模块符合预期,并能够正常运行。
以下是接入详情:
1. 按模型类型创建不同的模块结构
模型供应商下可能提供了不同的模型类型,例如 Openai 提供了llm 或 text_embedding 等模型类型。需在供应商模块下创建相应的子模块,确保每种模型类型有独立的逻辑分层,便于维护和扩展。
当前支持模型类型如下:
llm文本生成模型text_embedding文本Embedding模型rerankRerank 模型speech2text语音转文字tts文字转语音moderation审查
Anthropic 为例,系列模型内仅包含 LLM 类型模型,因此仅需在 /models 路径下新建 /llm 文件夹,并新增不同型号模型的 yaml 文件。详细代码结构请参考 GitHub 代码仓库。
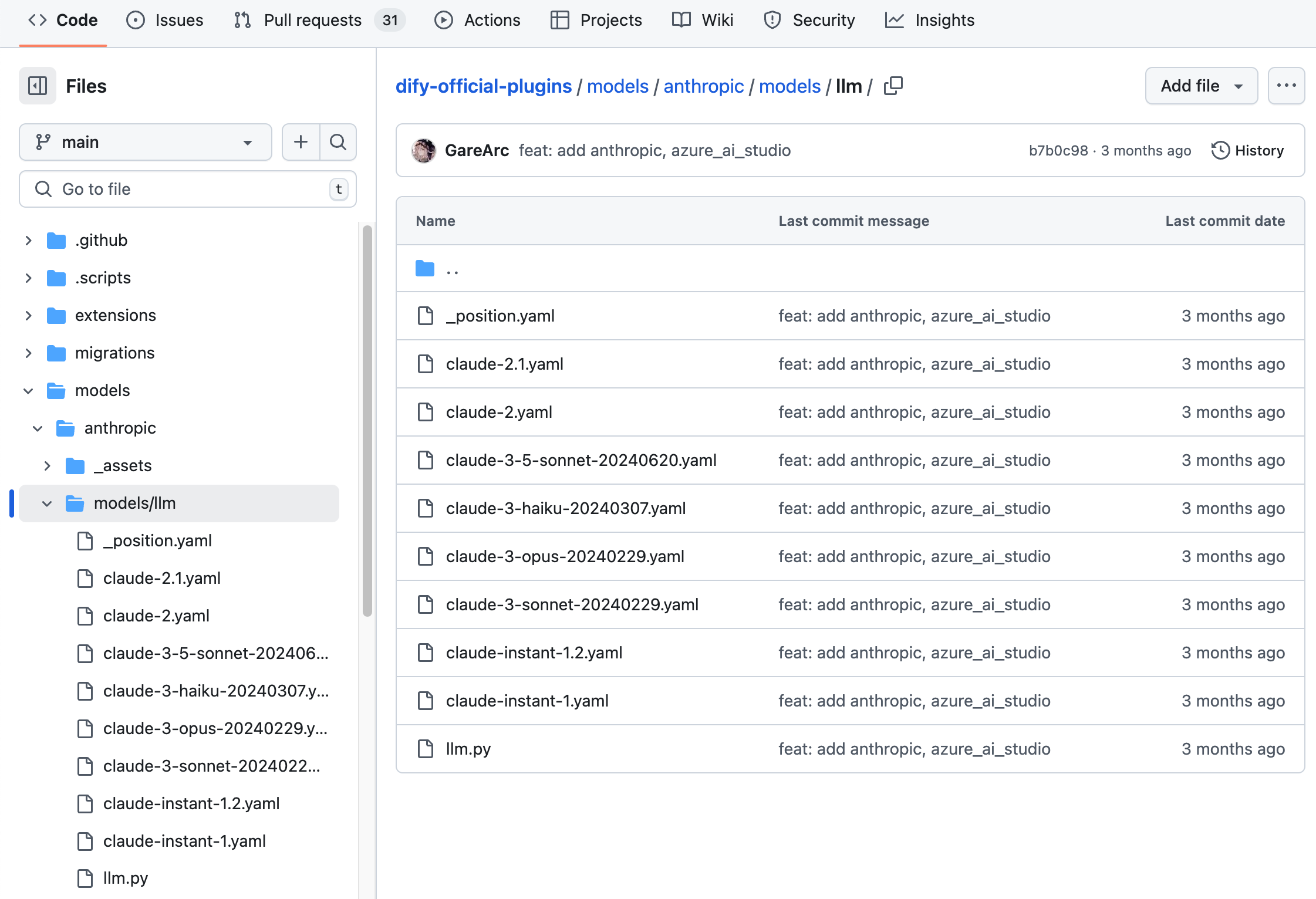
OpenAI 家族模型下包含 llm 和 text_embedding ,moderation,speech2text,tts 类模型,则需要在 /models 路径下为每种类型创建对应的文件夹。结构如下:
2. 编写模型调用代码
接下来需要在/models 路径下创建 llm.py 代码文件。以 Anthropic 为例,在 llm.py 中创建一个 Anthropic LLM 类并取名为 AnthropicLargeLanguageModel,继承 __base.large_language_model.LargeLanguageModel 基类。
以下是部分功能的示例代码:
- LLM 调用 请求 LLM 的核心方法,同时支持流式和同步返回。
yield 关键字的函数会被识别为生成器函数,其返回类型固定为 Generator。为了保证逻辑清晰并适应不同返回需求,同步返回和流式返回需要独立实现。
以下是示例代码(示例中参数进行了简化,实际实现时请根据完整参数列表编写):
- 预计算输入 tokens 数
- 调用异常错误映射表
InvokeError 类型,方便 Dify 针对不同错误做不同后续处理。
Runtime Errors:
InvokeConnectionError调用连接错误InvokeServerUnavailableError调用服务方不可用InvokeRateLimitError调用达到限额InvokeAuthorizationError调用鉴权失败InvokeBadRequestError调用传参有误
3. 添加预定义模型配置
如果供应商提供了预定义模型,为每个模型创建与模型名称同名的YAML 文件(例如 claude-3.5.yaml)。按照 AIModelEntity 的规范编写文件内容,描述模型的参数和功能。
claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620 模型示例代码:
4. 调试插件
接下来需测试插件是否可以正常运行。Dify 提供远程调试方式,前往“插件管理”页获取调试 Key 和远程服务器地址。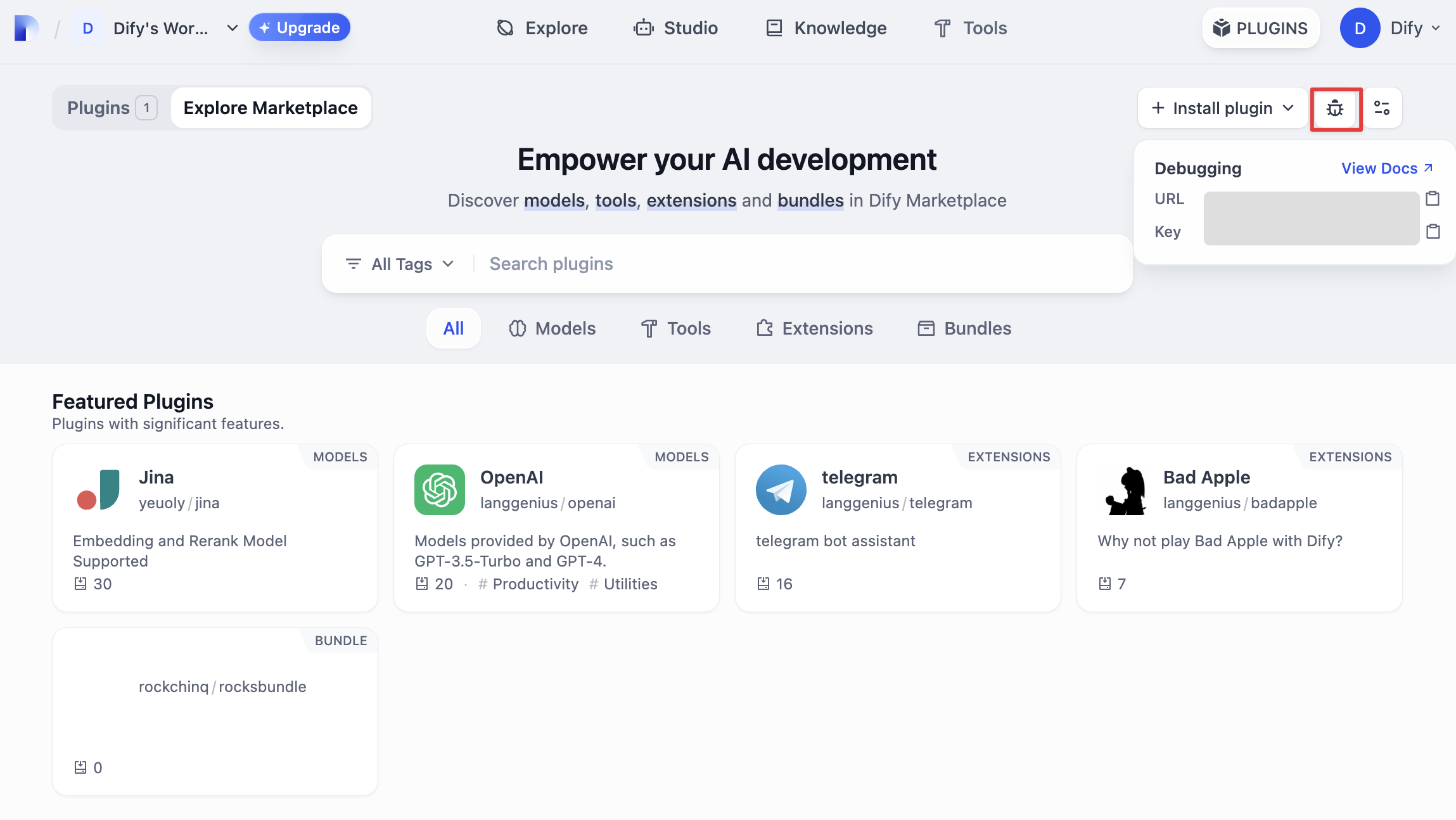 回到插件项目,拷贝
回到插件项目,拷贝 .env.example 文件并重命名为 .env,将获取的远程服务器地址和调试 Key 等信息填入其中。
.env 文件
python -m main 命令启动插件。在插件页即可看到该插件已被安装至 Workspace 内。其他团队成员也可以访问该插件。
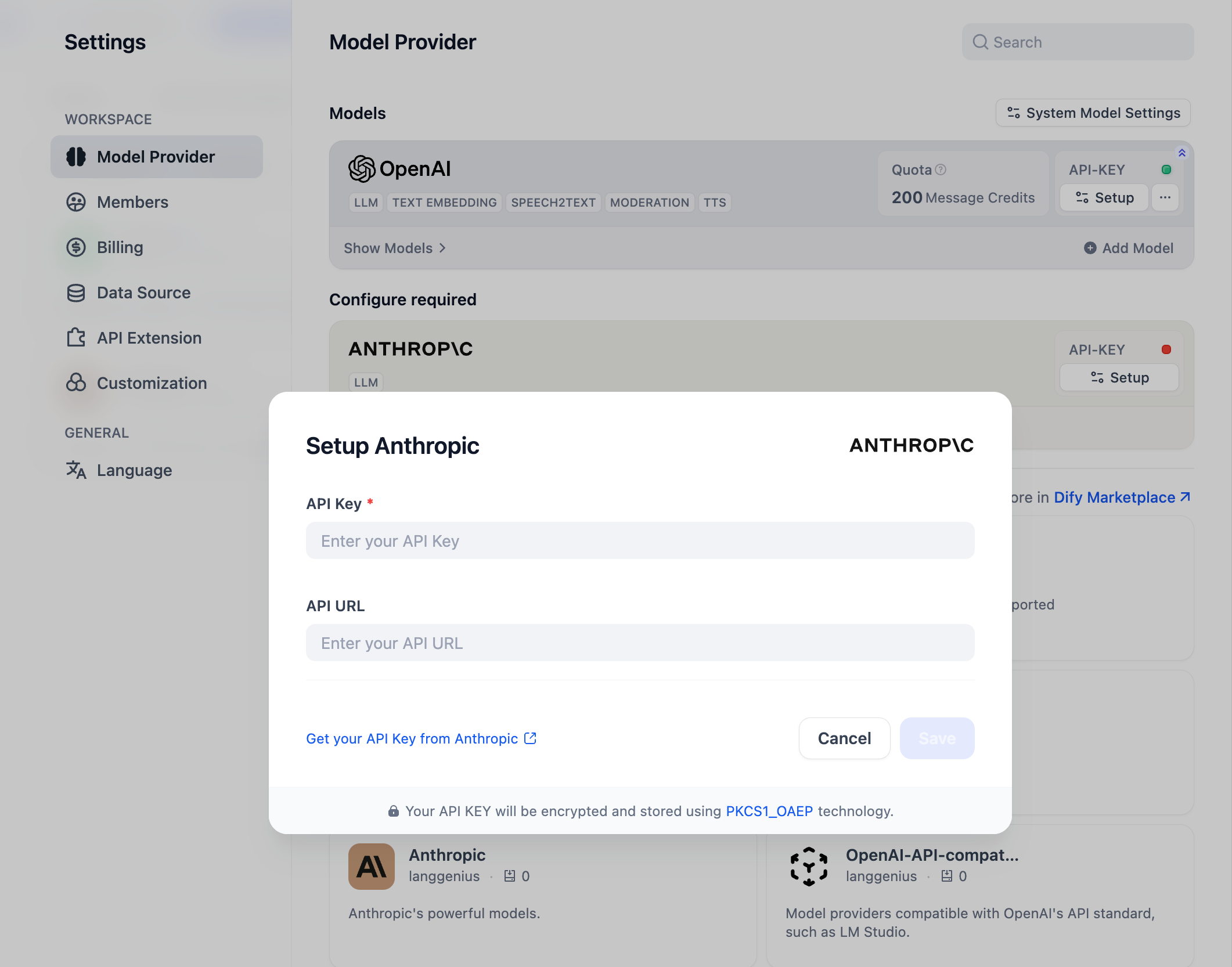
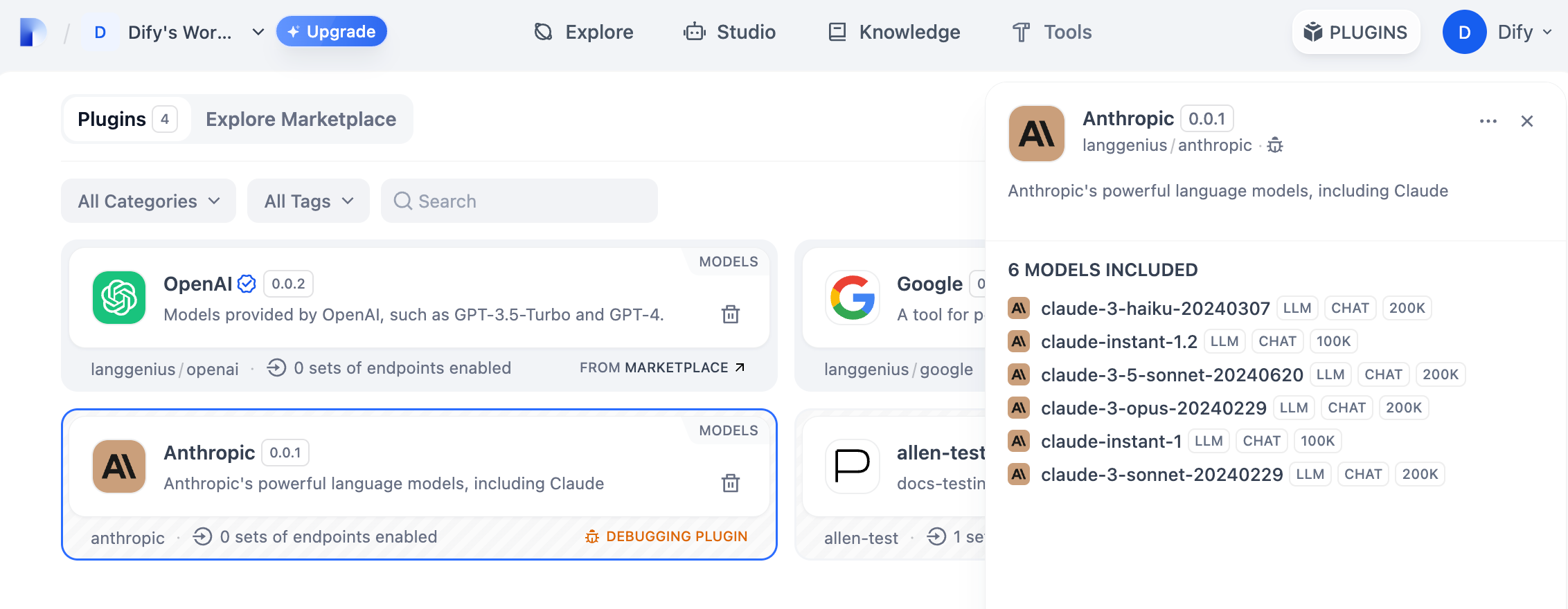 你可以在“设置” → “模型供应商”输入 API Key 以初始化该模型供应商。
你可以在“设置” → “模型供应商”输入 API Key 以初始化该模型供应商。
发布插件
现在可以将它上传至 Dify Plugins 代码仓库 来发布你的插件了!上传前,请确保你的插件遵循了插件发布规范。审核通过后,代码将合并至主分支并自动上线至 Dify Marketplace。探索更多
快速开始: 插件接口文档:- Manifest 结构
- Endpoint 详细定义
- 反向调用 Dify 能力
- 工具
- 模型
编辑此页面 | 提交问题

