Application Scenarios
1. Handling Network Exceptions
Example: In a workflow that retrieves and aggregates data from three API services (such as weather services, news summaries, and social media analysis), one service might fail to respond due to request limits, causing data retrieval to fail. With the error-handling function, the main process can continue using the data from the other two successful services while logging the failed API request. This log helps developers analyze the issue later and refine their service call strategies.2. Backup Workflow Design
Example: An LLM node tasked with generating detailed document summaries may encounter token limit errors when processing lengthy input. The workflow can switch to a backup path by setting the “Fail branch” on Error-handling Feature. For instance, a code node on the alternative path can split the content into smaller chunks and re-invoke the LLM node, preventing the workflow from breaking down.3. Predefined Error Messages
Example: When running a workflow, you might occasionally encounter a node returning vague error messages (such as a simple “request failed”), complicating pinpointing the issue quickly. Developers can write predefined error messages within the error handling feature to provide more explicit and more precise error information for subsequent application debugging.Error Handling Feature
The following four types of nodes have added error-handling feature. Click on the title to read the detailed documents: Retry on Failure Some exceptions can be resolved by retrying the node. In this case, you can enable the Retry on Failure feature in the node and set the number of max retries and the retry interval.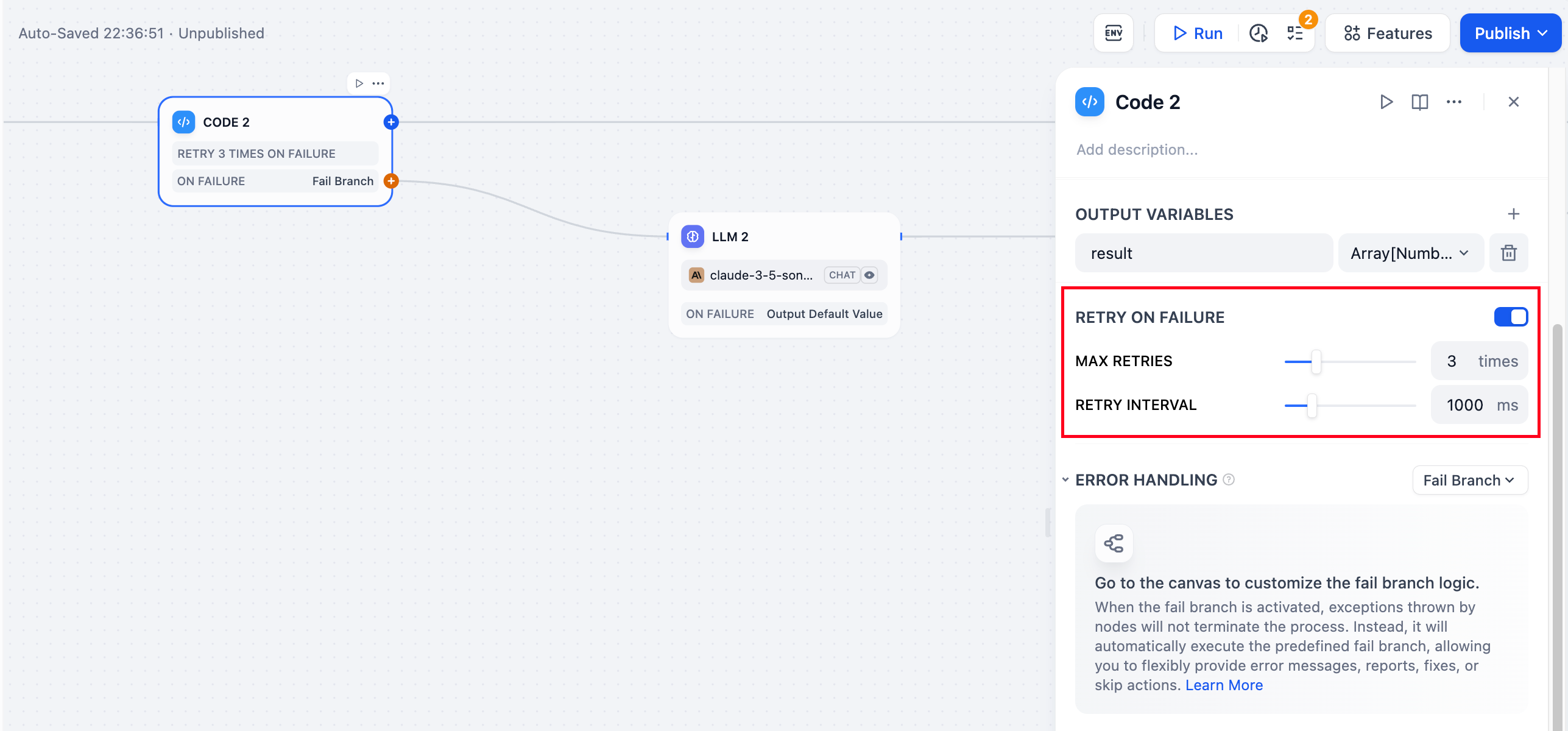 If an error is still reported after retrying the node, the next process will be run according to the predefined strategy in the Error Handling feature.
Error Handling
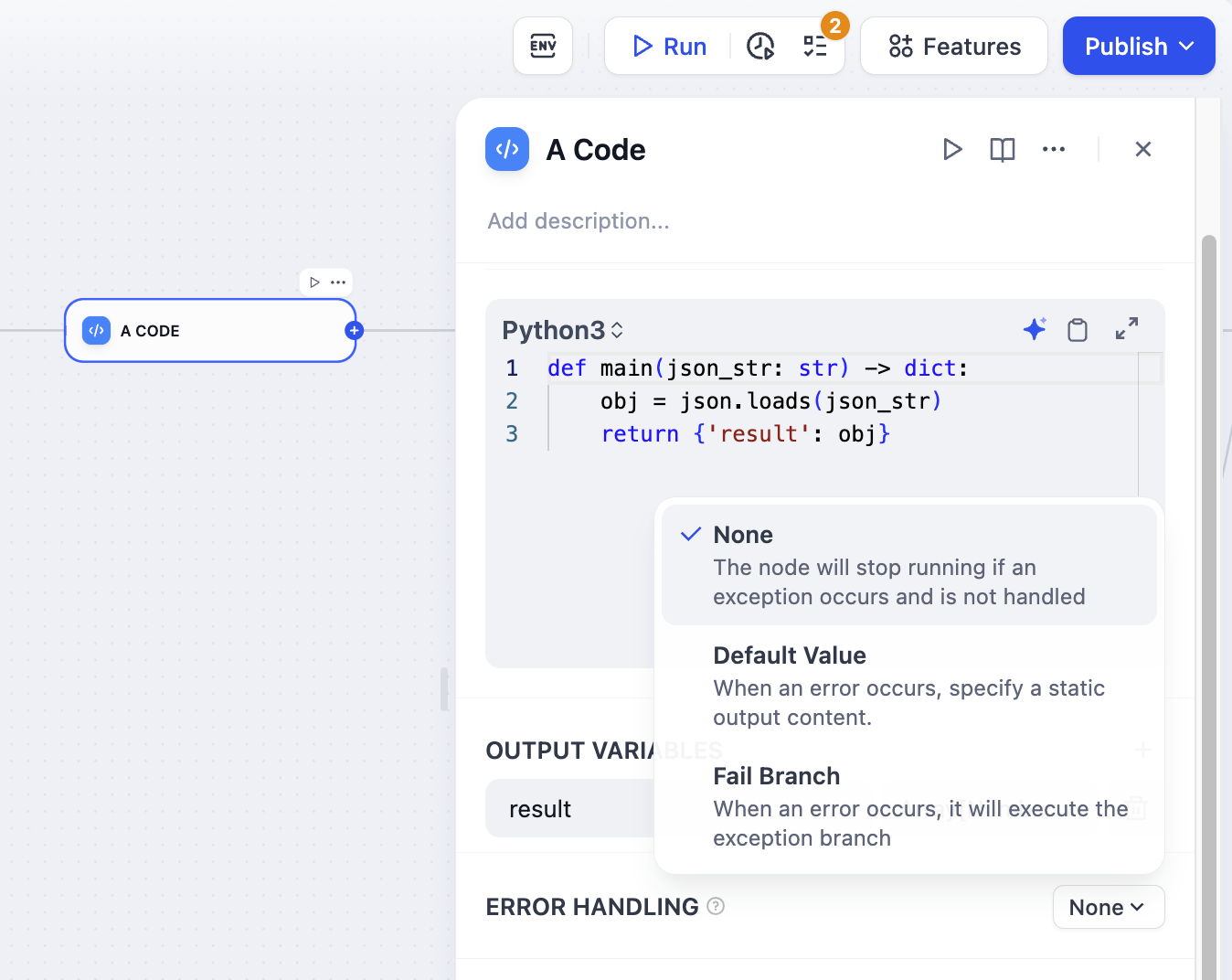
The error handling feature provides the following three options:
• None: Do not handle the exception, directly throw the node’s error message and interrupt the entire process.
• Default Value: Allows developers to predefine exception messages. After an exception occurs, use the predefined value to replace the original built-in error output message of the node.
• Fail Branch: Execute the pre-arranged fail branch after an exception occurs.
For explanations and configuration methods of each strategy, please refer to the predefined error handling logic.
If an error is still reported after retrying the node, the next process will be run according to the predefined strategy in the Error Handling feature.
Error Handling
The error handling feature provides the following three options:
• None: Do not handle the exception, directly throw the node’s error message and interrupt the entire process.
• Default Value: Allows developers to predefine exception messages. After an exception occurs, use the predefined value to replace the original built-in error output message of the node.
• Fail Branch: Execute the pre-arranged fail branch after an exception occurs.
For explanations and configuration methods of each strategy, please refer to the predefined error handling logic.
Quick Start
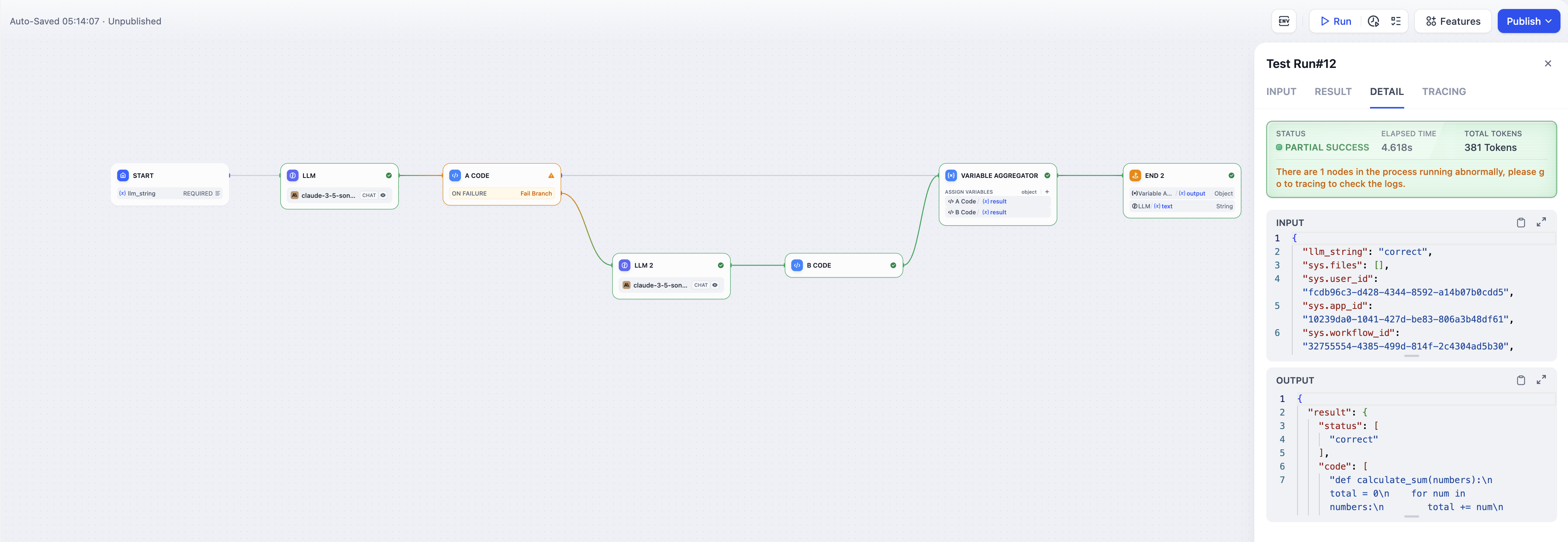
Scenario: Enabling Error-handling feature for Workflow Application Error Handling feature for Code Output in Workflow Applications The following example demonstrates how to implement error handling feature within a workflow application, using fail branch to handle node exceptions. The idea of the workflow design: An LLM node generates JSON code content (either correctly or incorrectly formatted) based on user’s input instructions, which is then executed and output through Code Node A. If Code Node A receives incorrectly formatted JSON content, it follows the predefined error handling design, executing the backup path while continuing the main process.- Creating a JSON Code Generation Node
- Enable Error Handling Feature for Node A
- Correct the Error Output from Node A
Click here to download the Demo DSL file.
Status Overview
In workflow applications, understanding both node and workflow status is crucial for effective monitoring and troubleshooting. Let’s explore how status indicators help developers track execution progress and handle exceptions efficiently.Node Status Types
- Success: Every node runs properly - the node completes its task and produces the expected output.
- Failure: When error handling isn’t enabled, the node stops working and reports an error.
- Exception: Even though an error occurs, the node doesn’t completely fail because error handling (either default values or alternative paths) kicks in to manage the situation.
Workflow Status Types
- Success: A perfect run - all nodes complete their tasks successfully, and the workflow produces the intended output.
- Failure: The workflow stops completely due to an unhandled node error.
- Partial Success: Think of this as a “managed failure” - while some nodes encounter issues, error handling mechanisms keep the workflow moving forward to completion.
FAQ
- What is the difference before and after enabling the exception handling mechanism?
Before Implementation
Without error handling, workflows are quite fragile:- A single node failure (like an LLM timeout or network hiccup) brings everything to a halt
- Developers must manually investigate and fix issues before restarting
- Creating workarounds means building complex, redundant safety nets
- Error messages tend to be vague and unhelpful
After Implementation
Error handling transforms your workflow into a more resilient system:- Workflows keep running even when things go wrong
- Developers can create custom responses for different types of errors
- The overall design becomes cleaner and more maintainable
- Detailed error logging makes troubleshooting much faster
- How to debug the execution of backup paths?

